The biological actions of Hypericum perforatum, also known as St. John’s wort
01/30/2018 / By Ralph Flores
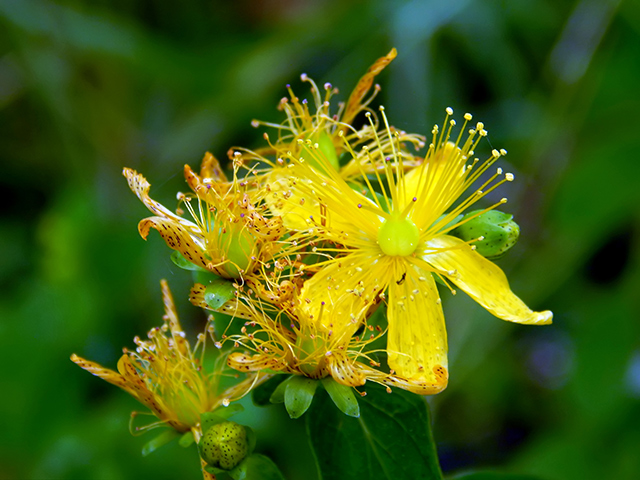

Researchers have discovered that extracts from the St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum L.), a plant that has been widely used in herbal treatment, contain antibacterial, antioxidant, and antimutagenic (prevents the alteration of a genetic material in a cell) properties. The study, which was published in the African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, tested the properties of the plant extract against bacteria strains which cause mastitis, a disease (usually caused by bacteria) which causes an inflammation of mammary glands.
- Researchers took H. perforatum flowers from Izmir, Turkey. These were taxonomically identified after and were stored in an herbarium.
- To make the extract, the flowers were thoroughly cleaned using flowing, distilled water. The materials were air-dried afterward and were pulverized in a “disruptive” mill. Prior to its use, the flowers were stored at four degrees Celsius. These were then extracted using a methanol solvent to produce an extract.
- For the study, extracts from the H. perforatum flowers were used against the mastitis bacteria — in particular, Staphylococcus aureus and the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS). The pathogens were subjected to 37 degrees Celsius over a 24-hour-period.
- To determine the antibacterial property of the extract, a Kirby-Bauer assay was used. After 24 hours, the inhibition zones around the discs were observed and compared against the controlled sample.
- The 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl-hydrate (DPPH) radical was used to evaluate the antioxidant properties of the H. perforatum extract by measuring the level of free radical activity of DPPH after the introduction of the extract, while for its antimutagenic properties, extracts were tested against a Salmonella Typhimurium assay.
- Results indicated that extracts from H. perforatum flowers were able to inhibit bacterial growth in both strains, via the formation of inhibition zones. The extract also managed to inhibit 32 percent of free radical activity based on the DPPH test. Additionally, H. perforatum displayed antimutagenic properties, displaying no mutagenic potentials based on the S. Typhimurium tests.
Overall, researchers report that H. perforatum extracts have medicinal properties that may potentially be used in cancer treatments.
Full text of study at this link.
Journal reference:
Gulten Okmen, Neslihan Balp?nar. THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF HYPERICUM PERFORATUM L. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 2017; 14: 1 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21010/ajtcam.v14i1.23
Tagged Under: Antibacterial activity, Antimutagenic activity, antioxidant activity, Herbs, mastitis, St. John's wort