Cupping therapy from ancient Traditional Persian Medicine found to improve quality of life
03/10/2018 / By David Williams
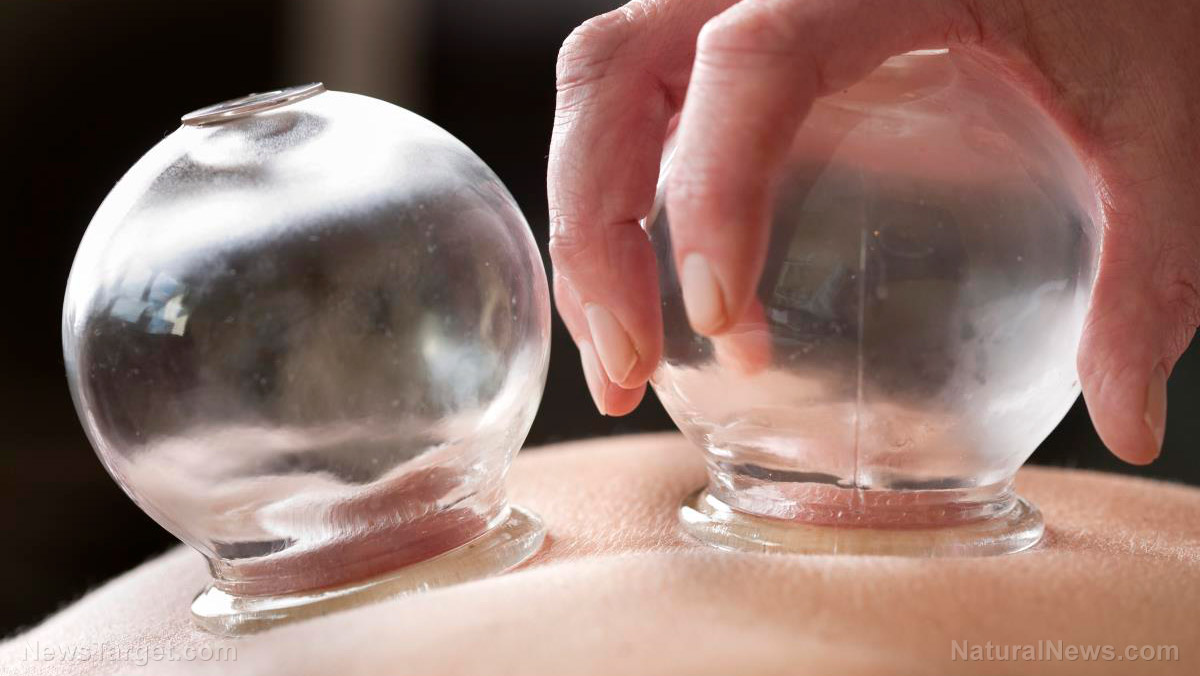

Most healthy individuals hardly ever have to worry about improving their current quality of life. After all, being healthy is reason enough to celebrate, and people typically are only healthy if their lives aren’t causing them a lot of stress. But if one tried, would it be possible to improve quality of life even further while in such a state?
Researchers from the Tehran University of Medical Sciences wanted to find out the answer to that question, so they conducted a study on participants who were located in Tehran, Iran, with a particular method in mind. The researchers set out to find whether cupping therapy, a practice that first originated in ancient China, can have any positive or negative effects in healthy individuals.
The details of the study, which was published in the Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, showed that cupping therapy can indeed increase the quality of life in individuals. And what’s interesting is that there were no serious adverse effects or, in fact, any negative consequences whatsoever.
The researchers noted that their study’s main objective was simply to determine the influence of cupping therapy on the quality of life of healthy patients that had been referred to traditional Persian medicine clinics located in Tehran. First, the study’s participants were examined by Traditional Persian Medicine (TPM) specialists, and their temperaments were determined for later reference. Then the cupping therapy sessions started for each and every one of them.
The official method used by the researchers was carried out thusly: the area of the back between the shoulders of participants was cleaned, and the actual act of cupping was performed with a disposable cupping glass for a few minutes. The participants were also asked to fill out a questionnaire before cupping and a full month after cupping, in order to determine their understanding of their own health status. The researchers then took all of the data they had and analyzed them in order to arrive at their conclusions.
The power of the elements: Discover Colloidal Silver Mouthwash with quality, natural ingredients like Sangre de Drago sap, black walnut hulls, menthol crystals and more. Zero artificial sweeteners, colors or alcohol. Learn more at the Health Ranger Store and help support this news site.
Based on the data that they gathered from the study’s participants, the researchers were able to conclude that nearly all of the participants felt that they had an increase in their quality of life after undergoing cupping therapy. To be more specific, from a pool of 178 participants with acceptable data from the project, scores of quality of life went up to 155, which represents 88 percent of all the patients.
Meanwhile, 21 participants felt that there were no changes to their quality of life, while only two noted a decrease in theirs. Quality of life, in this case, refers to a number of health conditions such as vitality, bodily pain, physical functioning, and mental health.
What’s even more interesting is that the study’s participants reported no major side effects. Perhaps the only noteworthy complications in the study were the pain and itching experienced by participants in the cupping area for about two to three days. This was to be expected and not counted as a major negative consequence. The lack of reports of hematoma caused by the cupping was also noted as a positive by the researchers. All in all, all of their data points towards the fact that cupping therapy can be extremely beneficial.
Of course, this has been a known fact for quite a long time now. Indeed, that’s why cupping therapy remains popular. It even had a resurgence recently due to the fact that athletes were using it to improve recovery and performance. Cupping therapy is also said to be effective as an alternative pain treatment, especially when combined with acupuncture. With this new study, it’s clear that it probably won’t fade away into obscurity any time soon.
Find out more methods derived from ancient Chinese medicine practices in ChineseMedicine.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: ancient china, ancient chinese medicine, cupping therapy, natural medicine, pain relief, pain therapy