Music and video use during high-intensity exercise alters perceived exertion
03/16/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

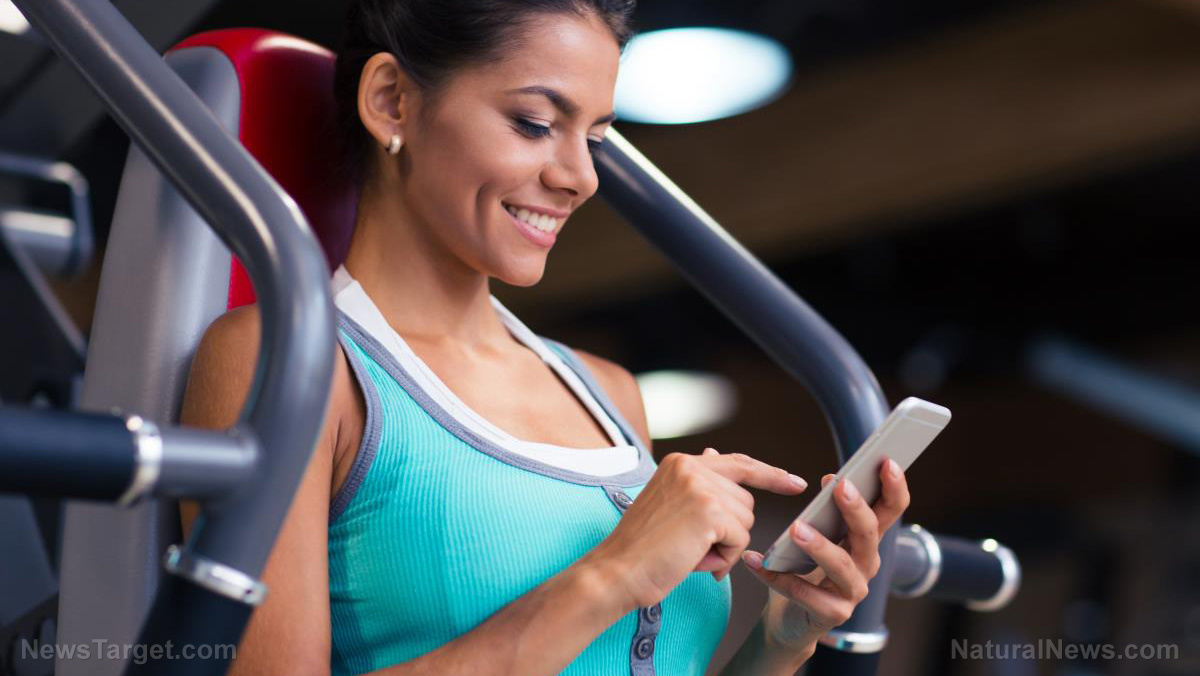
A study published in the Journal of Sport and Health Science has found that music and video affect a person’s perceived exertion. Study authors at the University of North Carolina in the U.S. looked at the impact of music and video on attentional focus and ratings of perceived exertion, or how hard a person feels like their body is working, during high-intensity exercise.
- The study involved 15 healthy men who finished a maximal fitness test in the first session to identify the workload necessary for high-intensity exercise to be executed in the succeeding sessions.
- After four days, the participants performed 20 minutes of high-intensity exercise either in a no-treatment control condition, while listening to music, watching a video, or both.
- The study authors took note of the participants’ attentional focus, ratings of perceived exertion, heart rate, and distance covered every four minutes of the exercise.
- Results revealed that the combination of music and video led to significantly lower ratings of perceived exertion, which means that the participants perceived they were working out less hard.
- In addition, the combination of music and video caused a significantly more dissociative focus compared to other combinations.
- The study authors believe that music and video can be used together to lower ratings of perceived exertion even when working out at a high intensity.
In conclusion, the findings of the study suggested that listening to music and watching a video while doing a high-intensity workout may lower a person’s perceived exertion and distract them from how hard their workout is.
For the full text of the study, go to this link.
Journal Reference:
Chow EC, Etnier JL. EFFECTS OF MUSIC AND VIDEO ON PERCEIVED EXERTION DURING HIGH-INTENSITY EXERCISE. Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2017; 6(1): 81-88. DOI: 10.1016/j.jshs.2015.12.007
Tagged Under: attention, attentional focus, distractions, exercise, fitness, focus, high-intensity exercise, mind-body medicine, music, perceived exertion, ratings of perceived exertion, RPE, video, workout