Study: Acupoint-stimulation just as effective as NSAIDs in reducing pain from dysmenorrhea
06/25/2018 / By Edsel Cook
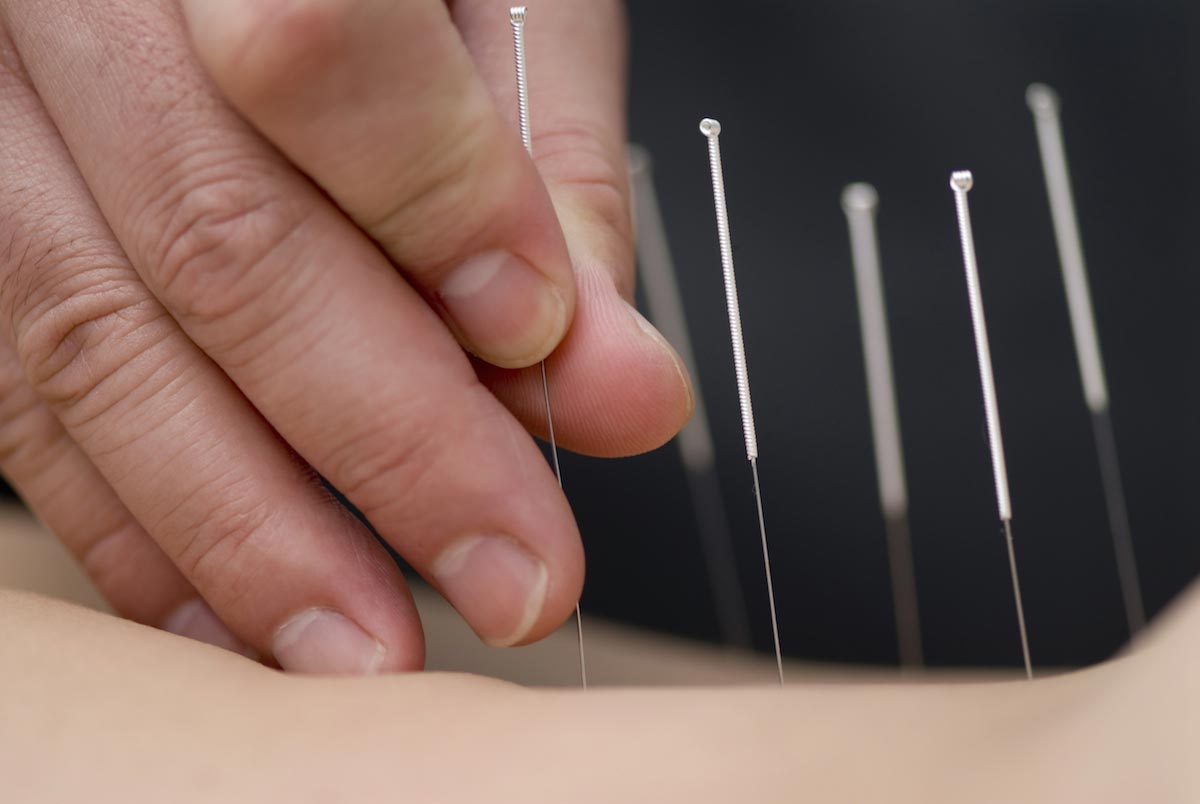
A Chinese review of assorted literature found that acupoint-stimulation possessed the potential to provide pain relief for cases of primary dysmenorrhea (PD). Furthermore, the traditional medical therapy compared favorably with conventional treatment that uses Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs).
Researchers from the Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine conducted the review. They published their findings in the scientific journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Six databases provided material that dated back to December 2014. The researchers selected randomized control trials that compared acupoint-stimulation with NSAIDs in the treatment of PD cases.
- The final list comprised 19 studies with a total of 1,679 PD patients. The control group consisted of patients who underwent NSAID treatment, while the other group comprised those who took acupoint-simulation.
- Comprehensive meta-analysis statistical software analyzed the studies based on five primary outcomes: The rate of clinical effectiveness, symptom score, visual analog score, variation in peripheral blood prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α), and side effects.
- The total efficacy of the PD patients who underwent acupoint-stimulation surpassed that of the NSAID-reliant control group. In addition, the therapy achieved positive effects in relieving the severity of the symptoms.
- The statistics of the two groups did not show any difference when it came to a reduction of the visual analog score (VAS) that indicates the degree of pain. However, the variation in PGF2α between the two groups was positive. The control group also experienced more side effects than the acupoint-stimulation group.
The full text of the study can be read here.
The researchers concluded that acupoint-stimulation is an effective means of relieving pain for patients who suffer from primary dysmenorrhea. They conclude that traditional Chinese medicine can serve as a complement for existing therapies or act as a non-pharmaceutical alternative.
Journal reference
Tagged Under: acupoint-stimulation, acupoints, acupuncture, alternative medicine, Chinese medicine, dysmenorrhea, menstruation, NSAID, NSAID treatment, NSAIDs, pain relief, pain relief medication, primary dysmenorrhea, traditional Chinese medicine