Evaluating the clinical efficacy of Chinese herbal Pulian ointment in treating psoriasis vulgaris
07/01/2018 / By RJ Jhonson
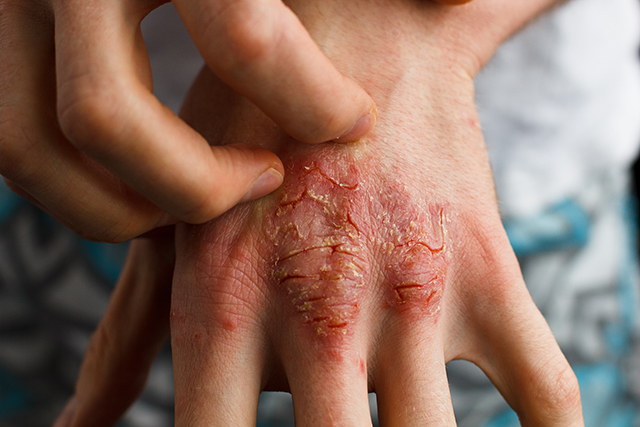
Pulian ointment, traditionally used in China to treat psoriasis, has been confirmed to be beneficial to sufferers of blood-heat psoriasis. A study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine details the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted to test the treatment’s effectiveness.
- Inpatients and outpatients from six centers were recruited for the study. The centers were: China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Dongfang Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Guang’anmen Hospital and Air Force General Hospital and Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA).
- Participants were selected using a stringent set of criteria and diagnosed of blood-heat psoriasis using uniform definitions.
- The 294 participants were divided into two groups: placebo and Pulian Ointment. Both groups were treated twice daily for four weeks and then scheduled for follow up after eight weeks.
- Psoriasis area severity index (PASI) scores, symptom severity and skin lesion area, and the quality of life were evaluated at baselines, two weeks, and four weeks.
- The researchers found improvements in both groups, especially in terms of PASI score at four weeks. Quality of life also improved. However, those in the placebo group showed a higher rate of relapse after eight weeks.
The researchers concluded that their findings proved the effectiveness of Pulian ointment and how well-tolerated it is by most patients. They recommended conducting a follow-up study to determine if preparation forms and greater intervention could improve the treatment’s therapeutic effects.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Li N, Zhao W, Xing J, Liu J, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Li Y, Liu W, Shi F, Bai Y. CHINESE HERBAL PULIAN OINTMENT IN TREATING PSORIASIS VULGARIS OF BLOOD-HEAT SYNDROME: A MULTI-CENTER, DOUBLE-BLIND, RANDOMIZED, PLACEBO-CONTROLLED TRIAL. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017;17(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1631-5
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, blood-heat psoriasis, blood-heat syndrome, Chinese medicine, herbal remedies, natural medicine, psoriasis, psoriasis treatment, psoriasis vulgaris, pulian ointment, skin health, traditional medicine