Analyzing the efficacy of three conservative treatments for lumbar spinal stenosis: Meditation, exercise and acupuncture
07/02/2018 / By RJ Jhonson
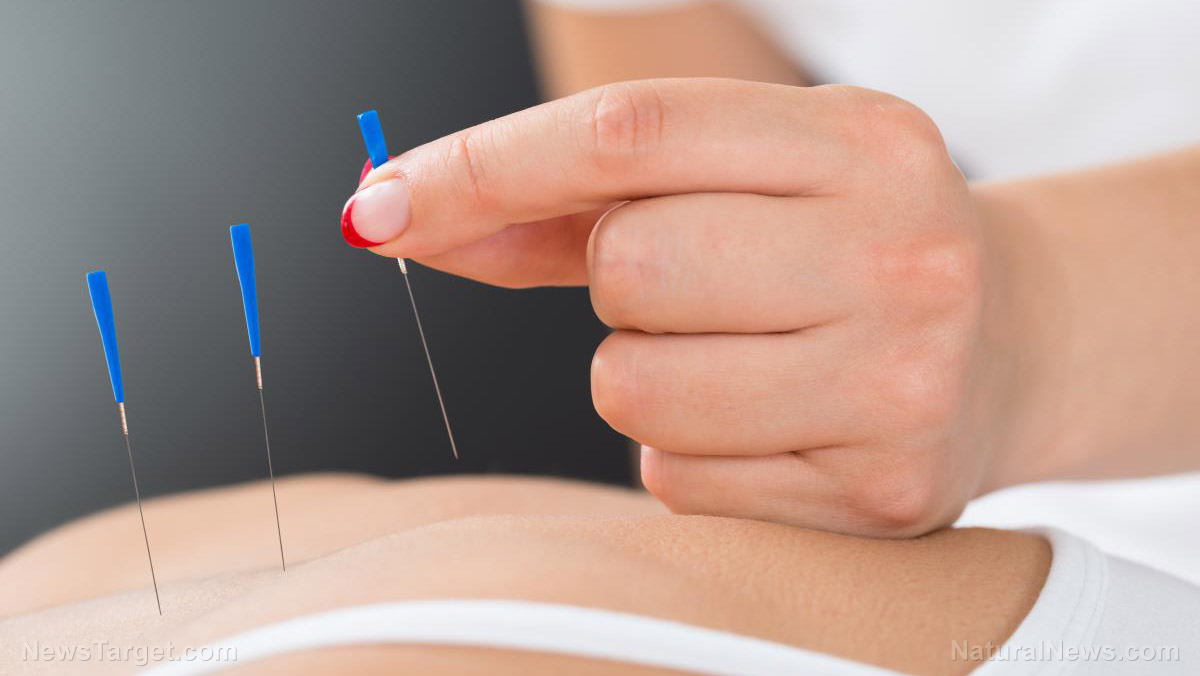
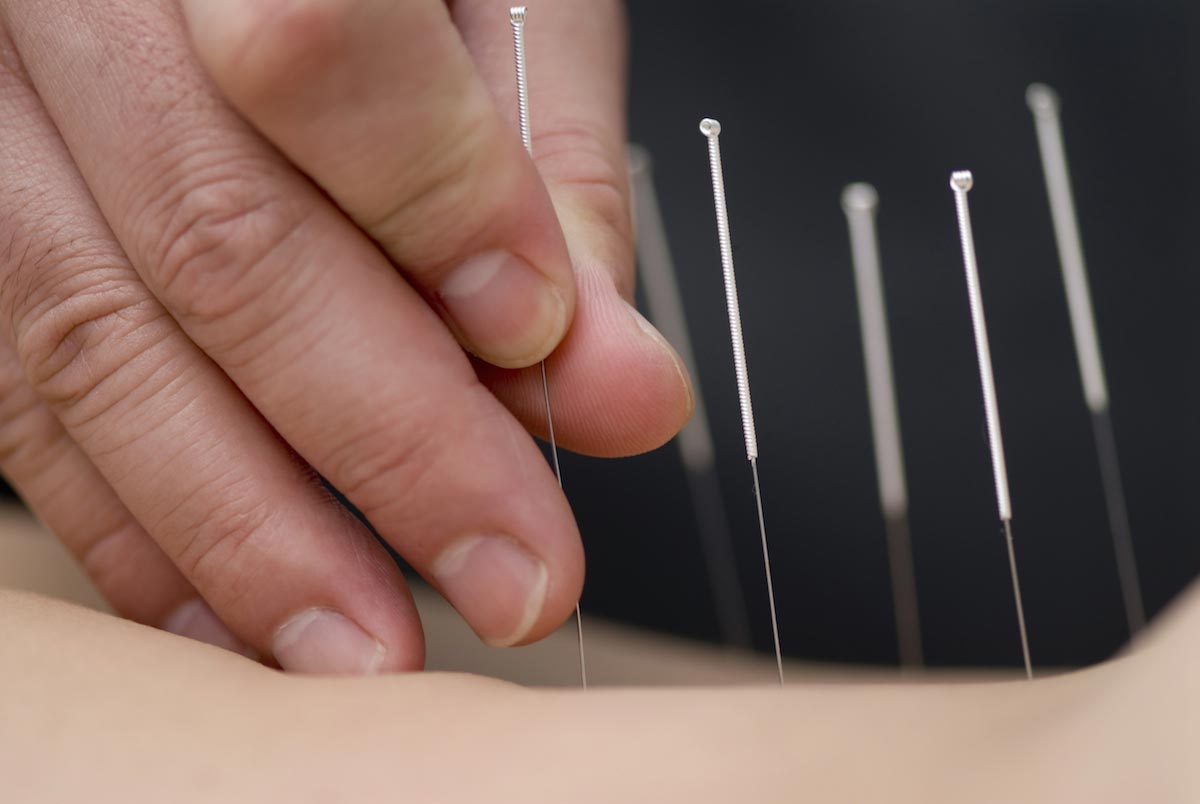
Acupuncture is among the most common methods used to treat back pain caused by lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). A study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine looks into its effectiveness relative to other methods of pain relief, specifically medication and exercise.
- The researchers recruited patients who went to Iwai Orthopaedic Medical Hospital from December 2011 to January 2014 for treatment of L5 root radiculopathy associated with LSS.
- The participants were randomly assigned to one of three groups: medication, exercise, and acupuncture. Subjects were recruited until each group had 38, 40, and 41 members respectively. The study lasted four weeks.
- The medication group was given 900 mg of acetaminophen that the members had to take three times a day. The exercise group had to six sets of flexion exercises, with each set being made of 10 reps. The acupuncture group went through two sessions on the first week and one session per succeeding week.
- All participants were required to fill out a Zurich claudication questionnaire (ZCQ) before and after four weeks of treatment.
- The participants in the acupuncture group expressed greater satisfaction in the treatment than did those in the other two groups. Their ZCQ scores also exhibited greater improvements in terms of both symptom severity and physical function.
The researchers concluded that their findings indicated proof of acupuncture’s superiority as a measure to relieve pain caused by LSS compared to medication and exercise.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Oka H, Matsudaira K, Takano Y, Kasuya D, Niiya M, Tonosu J, Fukushima M, Oshima Y, Fujii T, Tanaka S, et al. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THREE CONSERVATIVE TREATMENTS IN PATIENTS WITH LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS: LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS WITH ACUPUNCTURE AND PHYSICAL THERAPY STUDY (LAP STUDY). BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2018;18(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2087-y
Tagged Under: acupuncture, lumbar spinal stenosis, pain relief, spine