Analyzing the hepatoprotective activity of garden cress
07/13/2018 / By Edsel Cook
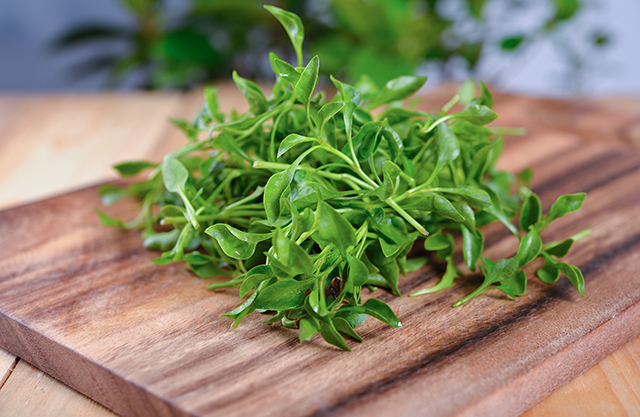

A recent Saudi study evaluated the garden cress (Lepidium sativum) for its ability to protect the liver from fulminant hepatic failure (FHF). They found that the plant’s ethanolic extract could provide a safe and effective means of managing hepatitis.
King Saud University sponsored the investigation. The findings were published in the science journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- A rat model was constructed to simulate a fulminant hepatic failure. D-galactosamine was administered to rats in order to simulate severe liver damage associated with acute hepatitis.
- Garden cress ethanolic extract doses of 150 and 300 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) were given to groups of rats. Another group received 25 mg/kg of silymarin as a positive control.
- Both garden cress extracts ameliorated liver damage by reducing serum and lipid peroxidation that caused cell-damaging oxidative stress. The effectiveness was deemed to be comparable to silymarin, an extract from milk thistle that possessed similar hepatoprotective abilities.
- The extracts improved the levels of oxidative stress markers and albumin, which were reduced due to D-galactosamine. In addition, they greatly reduced the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, up-regulated the IL-10 cytokine, and down-regulated the mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1).
- The garden cress extracts also mitigated myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and the ability of NF-κB to bind itself to DNA.
The researchers concluded that the ethanolic extract of garden cress could serve as a non-toxic means of improving the prognosis of FHF and reducing the significant mortality associated with the syndrome.
Find the full text of the study at this link. Or visit NaturalMedicines.news to read more articles about natural ways to protect your liver.
Read about more hepatoprotective plants and other natural ways to protect the liver at NaturalCures.news.
Journal Reference:
Raish M, Ahmad A, Alkharfy KM, Ahamad SR, Mohsin K, Al-Jenoobi FI, Al-Mohizea AM, Ansari MA. HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF LEPIDIUM SATIVUM SEEDS AGAINST D-GALACTOSAMINE/LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN ANIMAL MODEL. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016;16(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1483-4.
Tagged Under: Cress, fulminant hepatic failure, garden cress, Hepatitis, herbal medicines, Liver, liver damage, liver diseases, oxidative liver damage, oxidative stress, silymarin