Preparations from anthroposophical medicine demonstrate great antibacterial potential
10/03/2018 / By Ellaine Castillo
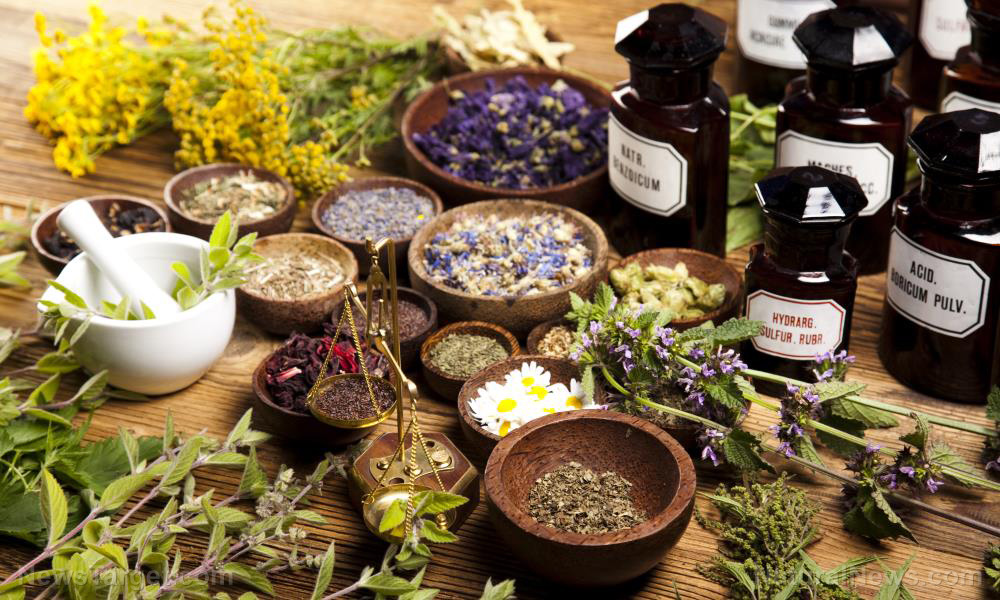

Researchers from the Center for Complementary Medicine and University Medical Center Freiburg discovered that Berberis Decoctum D2, a form of medication from anthroposophical medicine, exhibits antibacterial potential against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis. This study, which was published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, looked at the bactericidal property of different drugs from anthroposophical medicine to determine if they could serve as potential sources for new types of antibacterial compounds.
- Drugs from anthroposophical medicine are clinically used in German-speaking areas for the treatment of infectious diseases. However, no scientific claims have been made regarding their antimicrobial activity.
- Anthroposophical medicine preparations that met the following criteria were selected:
- No alcoholic content
- Prepared using only one plant
- Used for treating infectious diseases
- Among the different drugs from anthroposophical medicine, 33 were selected and subjected to tests for antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Additionally, growth kinetics and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) were also determined.
Results of the different tests showed that Berberis Decoctum D2, which was derived from Berberis vulgaris, exhibited antibacterial activity against S. aureus and B. subtilis, including methicillin-resistant strains. It was also determined that its antibacterial activity was selective against Gram-positive bacteria since the Gram-negative bacteria, E. coli and P. aeruginosa, were spared. These results show that Berberis Decoctum D2 has potential use beyond anthroposophical medicine.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
Learn more about the antibacterial potential medications from Anthroposophical Medicine by visiting AlternativeMedicine.news today.
Journal Reference:
Roser E, Gründemann C, Engels I, Huber R. ANTIBACTERIAL IN VITRO EFFECTS OF PREPARATIONS FROM ANTHROPOSOPHICAL MEDICINE. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 22 September 2016;16(372). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1350-3
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, Anthroposophical Medicine, Anthroposophical Medicine drugs, antibacteria, antibacterial property, Antimicrobial, Bacillus subtilis, bacterial infection, Berberis Decoctum D2, Berberis vulgaris, E. coli, infectious diseases, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus