Tartary buckwheat shown to improve lipid profile, reduce insulin resistance
05/14/2019 / By Ralph Flores
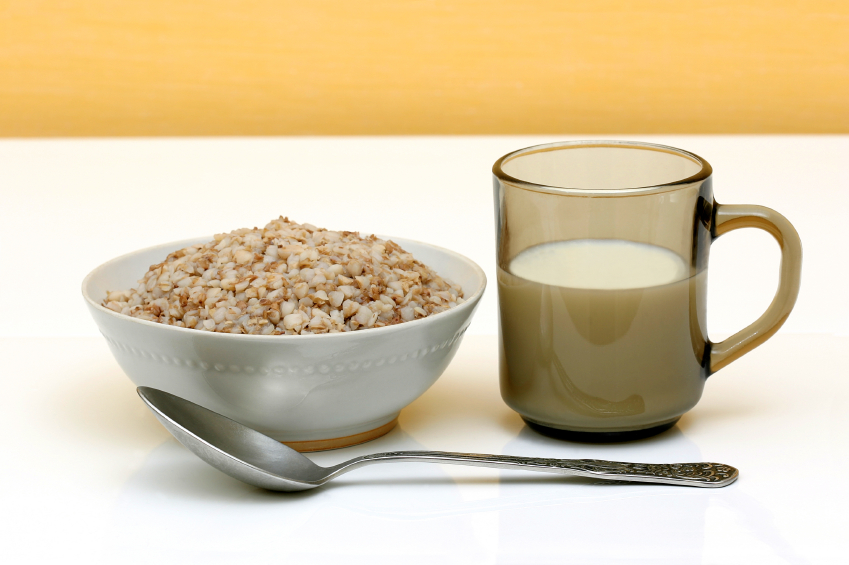

Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) can improve insulin resistance and lipid profile in people with Type 2 diabetes, according to a study published in Nutrition Research. The multi-university research investigated the effects of substituting certain foods with tartary buckwheat.
- Tartary buckwheat is nutrient-dense; it contains protein, dietary fiber, and flavonoids.
- Tartary buckwheat is also reported to improve Type 2 diabetes symptoms, based on in vivo tests; however, available research on whether it can be used as a whole food for Type 2 diabetics is limited.
- The researchers enrolled 165 patients with Type 2 diabetes in a parallel, randomized, open-label, controlled trial. The participants were assigned to either a control diet group, which received systematic diet plans and intensive nutritional education, or an intervention group, which had a portion of their staple food replaced with tartary buckwheat.
- Researchers also collected blood samples and diet information at baseline and after four weeks of intervention.
- Participants in the intervention group reported a decrease in their fasting insulin (2.46-2.39 Ln mU/L), total cholesterol (5.08-4.79 mmol/L), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (3.00-2.80 mmol/L) levels after four weeks. These results were better compared to those in the control diet group.
- Between the intervention and control groups, no significant differences in blood glucose or glycated hemoglobin levels were reported.
- Subgroup analysis also revealed that taking tartary buckwheat resulted in a dose-reduction of insulin, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but only in doses lower than 110 g/d.
In conclusion, taking tartary buckwheat can improve insulin resistance and lipid profile in patients with Type 2 diabetes.
Journal Reference:
Qiu J, Liu Y, Yue Y, Qin Y, Li Z. DIETARY TARTARY BUCKWHEAT INTAKE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND IMPROVES LIPID PROFILES IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES: A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL. Nutrition Research. December 2016;36(12):1392–1401. DOI: 10.1016/j.nutres.2016.11.007
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, anti-diabetes, cholesterol, dietary fiber, disease treatments, flavonoids, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, insulin, insulin resistance, Lipid profile, natural cures, natural medicine, nutrients, prevention, protein, research, tartary buckwheat, Type 2 Diabetes, whole food
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author