The role of gut microbiota on the biotransformation of Panax notoginseng saponins
11/05/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
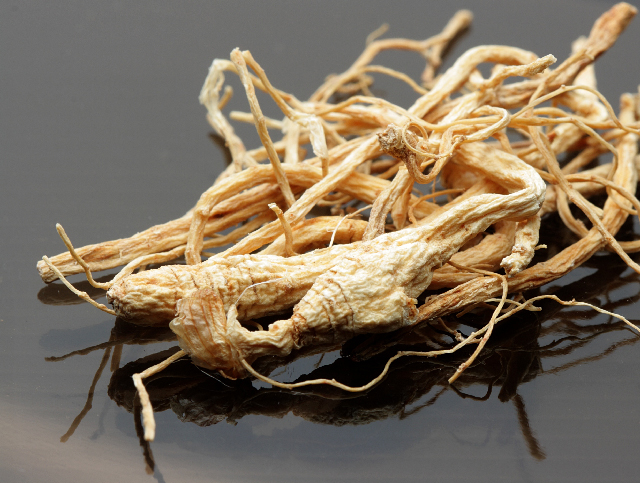

In this study, researchers from China investigated the gut microbiota-mediated transformation of Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) in vivo. The results of their study were published in the Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines.
- PNS are the major components of Panax notoginseng. They possess multiple pharmacological activities but poor oral bioavailability.
- While PNS can be metabolized by the gut microbiota in vitro, the exact role of gut microbiota in the metabolism of PNS in vivo is poorly understood.
- To address this, the researchers constructed pseudo-germ-free rat models using broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- They also developed a high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS) for quantitative analysis of four PNS metabolites, namely, ginsenoside F1 (GF1), ginsenoside Rh2 (GRh2), ginsenoside compound K (GCK), and protopanaxatriol (PPT).
- The researchers found that the four metabolites can be detected in the control rat plasma but not in the pseudo-germ-free rat plasma. This implied that PNS cannot be biotransformed effectively when gut microbiota is disrupted.
Based on their findings, the researchers concluded that gut microbiota plays an important role in the biotransformation of PNS into metabolites in vivo.
Journal Reference:
Guo YP, Chen MY, Shao L, Zhang W, Rao T, Zhou HH, Huang WH. QUANTIFICATION OF PANAX NOTOGINSENG SAPONINS METABOLITES IN RAT PLASMA WITH IN VIVO GUT MICROBIOTA-MEDIATED BIOTRANSFORMATION BY HPLC-MS/MS. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines. March 2019;17(3):231–240. DOI: 10.1016/s1875-5364(19)30026-3
Tagged Under: Chinese ginseng, gut health, gut microbiota, herbal medicine, natural medicine, Panax notoginseng, plant metabolites, research