Compounds from Calothamnus quadrifidus leaves found to exhibit antibacterial properties
11/11/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
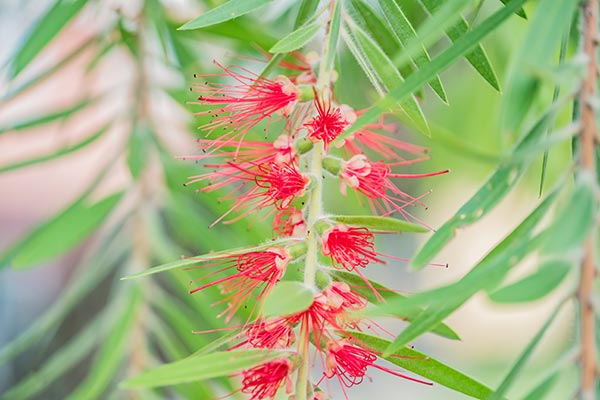

In this study, researchers from Helwan University in Egypt isolated triterpenoidal compounds from the dichloromethane fraction (DCMF) of Calothamnus quadrifidus leaves and evaluated their antibacterial activity. The results of their study were published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- C. quadrifidus has many traditional uses, but few studies have investigated its chemical and biological activities.
- For their study, the researchers used different chromatographic techniques to isolate pure triterpenoidal compounds from the DCMF of C. quadrifidus. They also used different chemical and spectroscopic techniques to identify each of these compounds.
- They evaluated the antibacterial activities of the compounds using agar well diffusion method and determined the minimum inhibitory concentration using microtiter plate assay method.
- The triterpenoids from the DCMF of C. quadrifidus leaves were identified as betulinic acid, ursolic acid, 3-acetyl-23-hydroxy betulinic acid, 2,23-dihydroxy betulinic acid, and 2,21,23-trihydroxy betulinic acid.
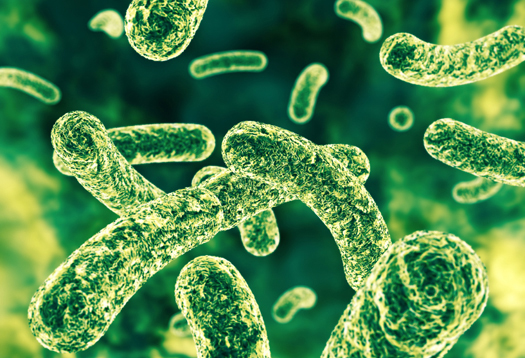
- Of these five compounds, the last two compounds showed strong antibacterial activity against Salmonella typhimurium and a moderate effect against Escherichia coli.
- Meanwhile, 3-acetyl-23-hydroxy betulinic acid and 2,23-dihydroxy betulinic acid showed a moderate effect against Staphylococcus aureus.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that the pure triterpenoidal compounds isolated from C. quadrificus leaves have antibacterial activities against different microorganisms.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Ibrahim HA, Elgindi MR, Ibrahim RR, El-Hosari DG. ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITIES OF TRITERPENOIDAL COMPOUNDS ISOLATED FROM CALOTHAMNUS QUADRIFIDUS LEAVES. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 09 May 2019;19(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2512-x
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural antibiotics, natural medicine, phytonutrients, prevention, remedies, research, triterpenoids