Green barley shows potential anti-cancer activity against colon cancer
02/05/2020 / By Ralph Flores
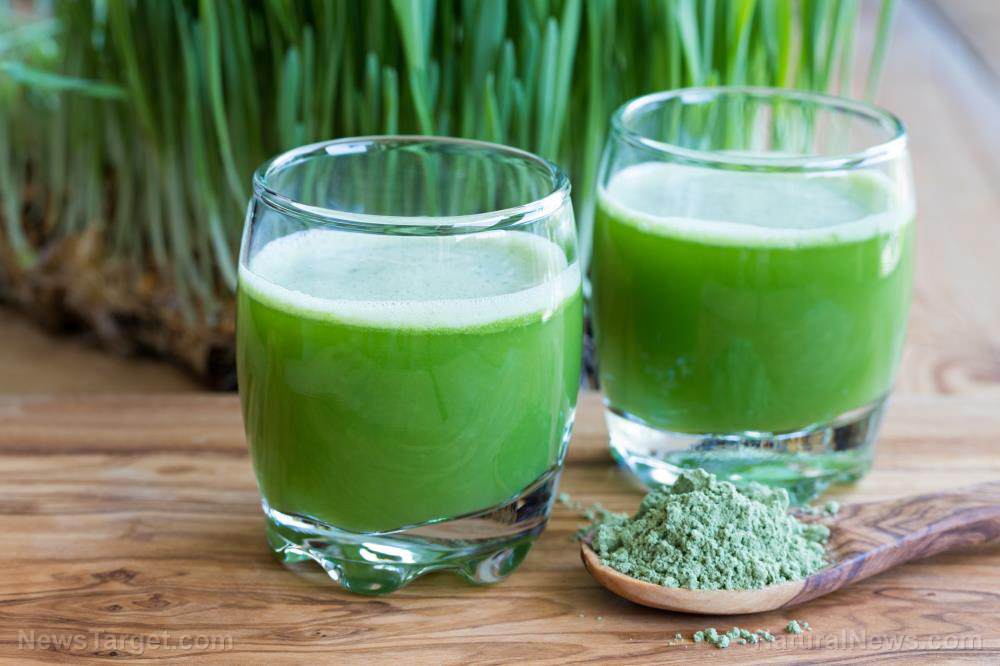

In this study, researchers from the Institute of Rural Health in Poland revealed that extracts from young green barley have anti-cancer properties. Their findings were published in the Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine.
- Young green barley contains essential nutrients. It also has a wide range of biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antidepressant, anti-atherosclerotic and anti-cancer activities.
- The researchers investigated the possibility of using green barley in colon cancer prevention.
- They obtained extracts from two commercial items: ground dried barley grass (YGB INT) and powder of young green barley juice (YGB GW). They used LDH and MTT assays to determine the effects of the barley extracts on the viability and proliferation on colon epithelial cells (CCD841 CoN).
- The researchers screened colon cancer cell lines (LS180, HT-29) using MTT and BrdU assays to determine the anti-cancer properties of the extracts. They also used May-Grunwald-Giemsa staining to determine any changes in cell morphology.
- The researchers found that the extracts were not cytotoxic to CCD841 CoN and did not affect cell proliferation and morphology.
- However, in colon cancer cells, both extracts significantly inhibited cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner.
- The BrdU test showed that both extracts have anti-proliferative properties, while the MTT test indicated that YGB GW had better anti-cancer activity.
- Light microscopy observation also revealed that both extracts can induce necrosis in LS180 and HT-29 cells.
In sum, YGB extracts can inhibit the proliferation of colon cancer cells without any adverse effects on colon epithelial cells.
Journal Reference:
Kawka K, Lemieszek M, Rzeski W. CHEMOPREVENTIVE PROPERTIES OF YOUNG GREEN BARLEY EXTRACTS IN IN VITRO MODEL OF COLON CANCER. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine. January 2019;26(1):174–181. DOI: 10.26444/aaem/102624
Tagged Under: anticancer, cancer cures, colon cancer, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, green barley, natural cures, natural medicine, research, Veggies