Efficacy of traditional remedies from Cameroon against antibiotic resistant bacteria
04/30/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
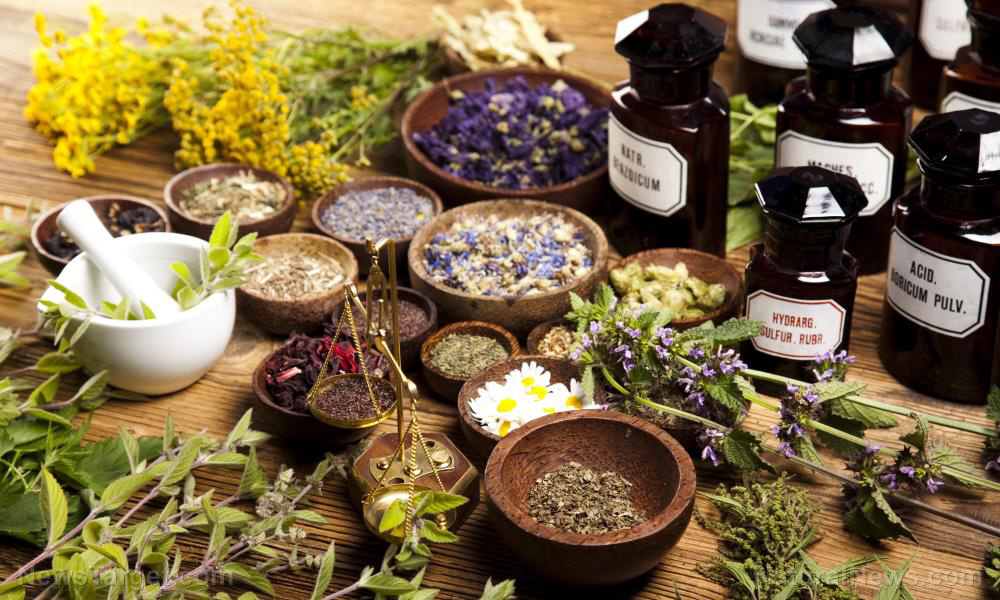

In this study, researchers at the University of Buea in Cameroon investigated the activity of ten remedies sold in marketplaces in Southwest Cameroon against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Their results were published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Traditional remedies are commonly used to treat various ailments, including bacterial infections.
- The researchers purchased ten remedies and analyzed their phytochemical components and microbial loads.
- They obtained methanol extracts from each remedy and tested their antibacterial activity using disc diffusion and microdilution.
- They also evaluated the cytotoxicity of the extracts using monkey kidney epithelial cells (LLC-MK2) and BALB/c mice.
- The researchers found that all the remedies had microbial loads above the acceptable limit (105?CFU/g).
- Extracts from four of the 10 remedies showed the high activity against the following clinical isolates:
- Citrobacter freundii
- C. youngae
- Enterobacter cloacae
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- P. vulgaris
- Providencia rettgeri
- Salmonella typhi
- Methycillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- Three of the four remedies also showed activity against four of the six control strains, namely, E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S. aureus, S. epidermidis and two different strains of S. enterica.
- The zones of inhibition of the remedies ranged from eight to 27 mm.
- Two of the four extracts produced at least 20?mm zones against multi-drug resistant C. freundii and E. coli but were less potent than the antibiotic gentamycin.
- The most active extracts had minimum inhibitory concentrations of 1 to 4 mg/mL.
- Only one extract showed bactericidal activity against MRSA, with a minimum bactericidal concentration of 8 mg/mL.
- Meanwhile, extracts from six remedies did not show cytotoxicity or cause any adverse effects in mice.
- Phytochemical screening revealed that the most active extracts contained high amounts of alkaloids and flavonoids.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that some remedies sold in marketplaces in Cameroon are safe and effective against infections caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Ngemenya MN, Djeukem GGR, Nyongbela KD, Bate PNN, Babiaka SB, Monya E, Kanso RK. MICROBIAL, PHYTOCHEMICAL, TOXICITY ANALYSES AND ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY AGAINST MULTIDRUG RESISTANT BACTERIA OF SOME TRADITIONAL REMEDIES SOLD IN BUEA SOUTHWEST CAMEROON. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 26 June 2019;19(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2563-z
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antibiotic resistance, bacterial infections, Cameroon, natural antibiotics, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients, remedies, research, superbugs