Ilex rotunda contains natural chemoprotective agents against colitis-associated cancer
11/05/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
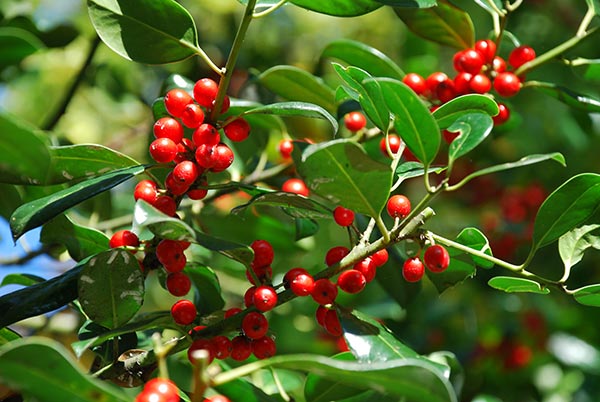

Researchers from China and Japan investigated the colitis-associated cancer (CAC)-preventive effect of the ethyl acetate extract of Ilex rotunda, commonly known as Kurogane holly. They reported their findings in an article published in the Journal of Natural Medicines.
- CAC is one of the most serious complications of inflammatory bowel disease.
- Its pathogenesis is poorly understood, and anti-inflammatory agents do not always prevent CAC, making it difficult to find effective treatments for it.
- I. rotunda is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine used clinically to treat intestinal disease.
- Using nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) translocation model in Caco-2 cells, the researchers screened the ethyl acetate extracts of I. rotunda for potential CAC-preventive agents.
- They chose this model because activated NF-kB can be used by tumor cells at the early stage of tumorigenesis.
- The researchers isolated 24 components from the extract and identified them via multiple chromatography and spectral analyses.
- MTT experiments in IEC-6 and RAW264.7 cells revealed that all 24 compounds were non-toxic to normal cells.
- The researchers also found that one of the compounds, rotundic acid (RA), can inhibit LPS-induced NF-kB translocation in Caco-2 cells.
- Additionally, RA did not induce apoptosis in Caco-2 tumor cells but showed anti-inflammatory activity in immune and intestinal epithelium cells (RAW264.7 and IEC-6 cells).
- On the other hand, the removal of RA and its 28-O-glucopyranoside from the extract reduced its in vivo CAC-preventive activity.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that RA in the ethyl acetate extract of I. rotunda is a potential therapeutic agent against colitis-associated cancer.
Journal Reference:
Han Y, Zhang L, Li W, Liu X, Xiao J, Chen G, Li N. NATURAL CAC CHEMOPREVENTIVE AGENTS FROM ILEX ROTUNDA THUNB. Journal of Natural Medicines. 13 February 2019;73(3):456–467. DOI: 10.1007/s11418-019-01281-z
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, cancer treatment, Chinese medicine, colitis-associated cancer, gut health, herbal medicine, Herbs, Kurogane holly, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author