Federal review targets U.S. childhood vaccine schedule far exceeding other developed nations
12/08/2025 / By Cassie B.
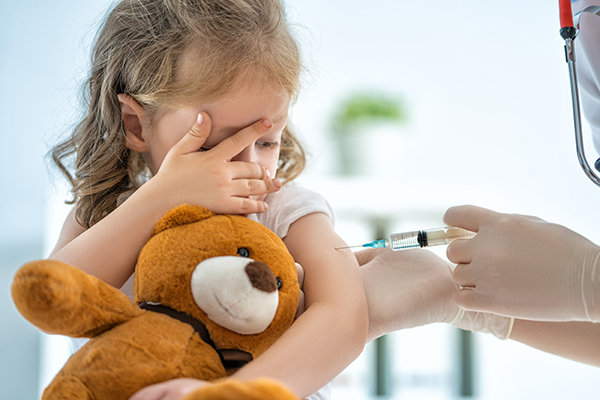

- President Trump orders a review of the U.S. childhood vaccine schedule.
- The CDC panel ends the universal newborn hepatitis B vaccine recommendation.
- Critics argue the schedule lacks long-term safety testing for cumulative effects.
- The review will compare U.S. practices to countries with fewer vaccine doses.
- Aluminum adjuvant exposure in infants is cited as a key safety concern.
In a move that challenges decades of public health orthodoxy, President Donald Trump has ordered a top-to-bottom review of the U.S. childhood immunization schedule, demanding to know why American children are recommended to get shots for 18 diseases while peer nations recommend far fewer. The directive, issued Friday, instructs the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to compare U.S. practices with countries like Denmark, Japan, and Germany and to adopt foreign policies deemed more scientifically sound. This seismic shift comes just hours after a key CDC advisory panel voted to end the universal recommendation that all newborns receive the hepatitis B vaccine within their first day of life.
The president’s memorandum frames the U.S. as a glaring outlier, stating, “In January 2025, the United States recommended vaccinating all children for 18 diseases… making our country a high outlier in the number of vaccinations recommended for all children.” The review will be led by HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a longtime critic of the vaccine schedule’s density and timing, alongside CDC Director Mandy Cohen. This action signals a profound willingness to question the “one-size-fits-all” approach that has defined American pediatric care for generations.
This policy shift did not occur in a vacuum. It follows intense scrutiny from medical professionals and advocates who argue the expansive schedule has never been rigorously tested for cumulative safety. Attorney Aaron Siri, who recently addressed the CDC’s advisory committee, argued that the liability shield granted to vaccine manufacturers in 1986 removed the economic incentive for robust long-term safety studies. “When it comes to routine childhood vaccines … they don’t have those same concerns,” Siri stated, noting the schedule exploded from three to 72 doses after the law was passed.
The data presented to health officials underscores the divide. Dr. Tracy Beth Høeg, now acting director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, highlighted that while U.S. children receive 72 core vaccine doses, children in Denmark receive just 11. “Why are we so different from other developed nations, and is it ethically and scientifically justified?” Høeg asked during a recent session. She pointed out that this increased load results in U.S. children being exposed to significantly more aluminum adjuvants—5.9 milligrams by age two compared to Denmark’s 1.4 milligrams.
A closer look at aluminum
The aluminum exposure is a central concern for many critics. Aluminum salts are used in vaccines to provoke an immune response, but their safety profile in the developing bodies of infants is hotly debated. Dr. Evelyn Griffin, an OB/GYN advising the CDC, acknowledged that the mechanisms of aluminum adjuvants “are not fully understood” and that only one small study has examined aluminum in infants’ blood post-vaccination. She concluded that aluminum accumulation is “a warranted concern,” a significant admission from within the advisory structure.
The now-rescinded hepatitis B mandate for newborns epitomized the concerns driving this review. For years, doctors like Paul Thomas have argued the vaccine is inappropriate for most infants. “Hepatitis B is a sexually transmitted disease or acquired through IV drug use; newborns have zero risk for these behaviors,” Thomas noted. The CDC’s own excipient list shows the vaccine contains aluminum and formaldehyde, a known carcinogen. Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has cited internal CDC analysis from the late 1990s that found an alarming 1,135% increased relative risk of an autism diagnosis following timely hepatitis B vaccination, data which led to secret meetings and a reported cover-up.
The global standard
The review ordered by President Trump seeks to align U.S. policy with a global standard that appears more restrained. The president called the American schedule, which he said long required 72 “jabs,” “ridiculous” and asserted that “many parents and scientists have been questioning the efficacy of this ‘schedule.’” His directive to “fast track” the evaluation places the burden on health agencies to prove their recommendations are the “gold standard of science and common sense,” as he put it.
This moment represents a potential turning point. It moves the conversation from fringe forums to the highest levels of government, demanding accountability for a schedule that has expanded largely without concurrent long-term safety surveillance. As Høeg stated, U.S. agencies owe American children recommendations that are “based on data and not politics.”
The fundamental question now is whether a system built on mandates and a dense schedule will yield to a model prioritizing individualized risk assessment and truly robust safety science. For countless parents who have felt coerced and ignored, this review is a long-overdue validation.
Sources for this article include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
Adjuvants, awakening, big government, Big Pharma, CDC, children's health, Donald Trump, health freedom, Hepatitis B vaccine, immunization, infant's health, medical extremism, pharmaceutical fraud, progress, rational, real investigations, research, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., skeptics, vaccine schedule, vaccine wars, vaccines
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author