Understanding the physiochemical properties of burnet
05/21/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
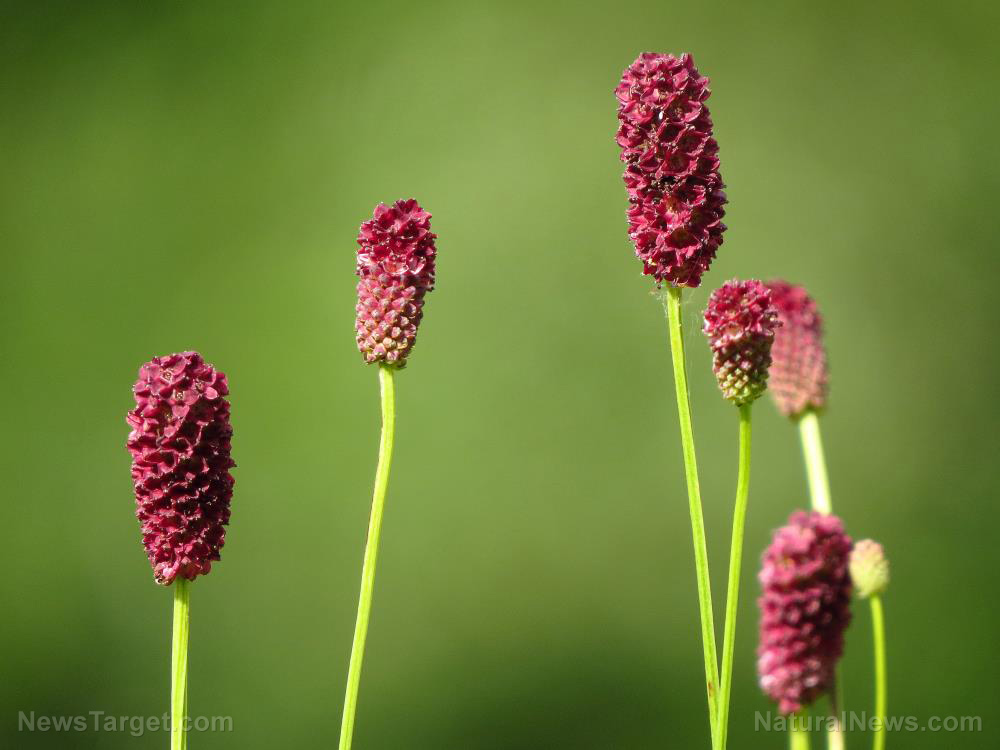

In this article, researchers from the Northwest University in China review the advances in botanical, phytochemical, and pharmacological studies conducted on plants from the genus Sanguisorba (burnet). Their review was published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
- According to the researchers, plants from the genus Sanguisorba have been considered as medicinal ingredients for over 2,000 years.
- More than 120 chemical constituents have been isolated and identified from these plants, especially from S. officinalis and S. minor.
- Triterpenoids, phenols, and flavonoids are the primary bioactive constituents of these plants.
- Triterpenoids can be used as quality control markers to determine the quality of medicinal materials and their preparations.
- Plants from the genus Sanguisorba exhibit a wide range of pharmacological properties, including hemostatic, antibacterial, antitumor, neuroprotective, and hypoglycemic activities in vitro and in vivo.
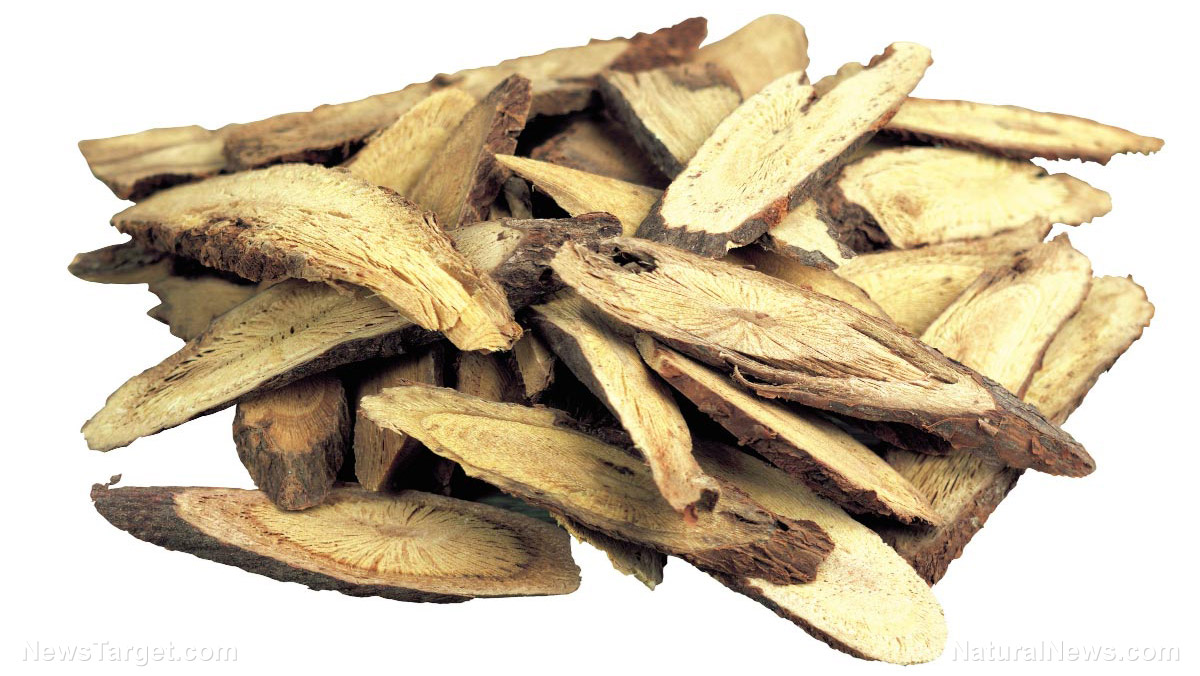
- In Chinese medical practice, many drugs (e.g., tablets and powders) that contain S. officinalis roots have been used to treat leukopenia, hemorrhaging, and burns.
- There is still a multitude of Sanguisorba species that have garnered little or no attention.
- The researchers can find very few reports concerning the clinical use and toxic effects of these plants.
In conclusion, the researchers believe that further attention should be focused on the study of plants from the genus Sanguisorba to learn more about their respective toxicology data, any relevant quality-control measures, and the clinical value of their crude extracts, active compounds, and bioactive metabolites.
Journal Reference:
Zhao Z, He X, Zhang Q, Wei X, Huang L, Fang JC, Wang X, Zhao M, Bai Y, Zheng X. TRADITIONAL USES, CHEMICAL CONSTITUENTS AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF PLANTS FROM THE GENUS SANGUISORBA L. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2017;45(02):199–224. DOI: 10.1142/s0192415x17500136
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, burnet, burnet roots, disease treatments, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, greater burnet, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, phytochemicals, remedies, research, salad burnet, sanguisorba, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine