Looking to get shredded? Try supplementing with ginseng
05/22/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
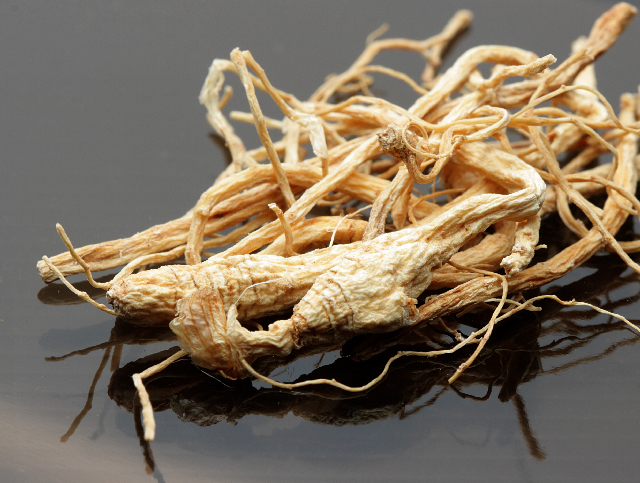

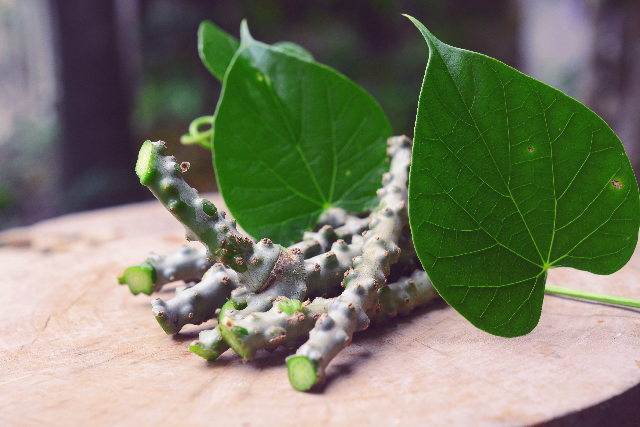
People into resistance training may want to consider taking ginseng. A study published in the journal Nutrition Research found that ginseng contains a compound called panaxatriol that helps promote muscle protein synthesis after an intense exercise.
Muscle protein synthesis is a naturally occurring process wherein protein is produced to repair muscle damage caused by vigorous exercises like resistance training. Enhanced muscle protein synthesis has been linked to improved muscle growth and muscle repair.
In the study, researchers from Japan hypothesized that panaxatriol derived from ginseng triggers the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling and muscle protein synthesis by activating both the Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling pathways and that panaxatriol promotes muscle protein synthesis when combined with resistance exercise. To test their hypothesis, the researchers divided rats into control, panaxatriol-only, exercise-only, and exercise and panaxatriol groups. They administered 0.2 grams per kilogram (g/kg) of panaxatriol to rats in the panaxatriol and exercise group immediately after exercise.
The results revealed that the administration of panaxatriol significantly increased muscle protein synthesis three hours after exercise via mTORC1 signaling in rat skeletal muscle. Based on the findings of the study, the researchers concluded that panaxatriol derived from ginseng might be used to enhance muscle protein synthesis after resistance exercise.
Earlier studies have also shown that supplementing with ginseng may be beneficial for exercise. A review of studies on herbal sports supplements published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition has reported that ginseng supplementation enhances muscular strength and increases endurance. Another study, which was conducted by researchers at the University of Chieti in Italy, also revealed that supplementation with ginseng effectively improves aerobic capacity, oxygen consumption, total workload, time to exhaustion, and ventilation. (Related: Korean ginseng prevents oxidative stress caused by work.)
Mother Nature's micronutrient secret: Organic Broccoli Sprout Capsules now available, delivering 280mg of high-density nutrition, including the extraordinary "sulforaphane" and "glucosinolate" nutrients found only in cruciferous healing foods. Every lot laboratory tested. See availability here.
More reasons to take ginseng
Ginseng has also been associated with other health benefits. In addition to improving exercise, you can take ginseng to:
- Increase energy. There is some evidence suggesting that ginseng may help promote physical and mental activity in people who feel weak and tired. Ginseng has also been shown to help cancer patients with fatigue.
- Boost brain function. Ginseng may also be used to improve cognition and thinking. In a study published in The Cochrane Library, ginseng appeared to improve cognition, behavior, and quality of life of participants.
- Reduce inflammation. The herb is also often used to reduce inflammation. A study published in the Journal of Translational Medicine has found that ginseng contains ginsenosides that may have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Lower blood sugar: Ginseng appears to be beneficial for people with and without diabetes in terms of controlling blood sugar levels. A study published in the Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine has shown that American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) and Asian ginseng (P. ginseng) can enhance the functioning of pancreatic cells, increase insulin production, and improve blood sugar uptake in tissues. Korean red ginseng has also been shown to improve glucose and insulin regulation in people with Type 2 diabetes, according to a study published in the journal Nutrition, Metabolism & Cardiovascular Diseases. Another study has suggested that fermented red ginseng was even more effective at controlling blood sugar. The study, which was published in the Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, noted that fermenting the herb with live bacteria can turn ginsenosides from ginseng into a more easily absorbed and potent form.
Adding ginseng to your diet is easy. You can eat ginseng root raw or lightly steamed. You can also make tea from it by stewing freshly sliced ginseng in water. Moreover, the herb can be added as an ingredient to soups and stir-frys, while its extract is available in capsule, oil, powder, and tablet forms.
Learn more about the health benefits of ginseng by going to Herbs.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: exercise, ginseng, herbal medicine, Herbs, muscle, muscle protein synthesis, natural cures, natural medicine, natural treatment, panaxatriol, resistance exercise, supplement