Exploring the physicochemical composition of the essential oil of galangal
05/23/2019 / By Janine Acero
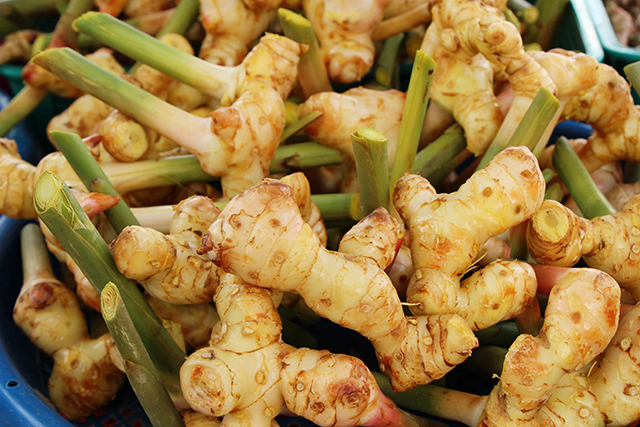

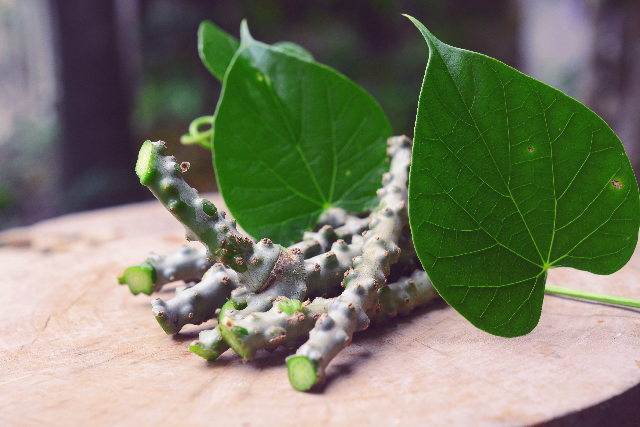
Researchers from India investigated the physicochemical composition of the essential oil of Kaempferia galanga L., commonly known as aromatic ginger. Their findings appeared in the Journal of Essential Oil Research.
- K. galanga L., known by other names such as Kacholam and Kencur, is a medicinal plant of India that is widely used in the preparation of both traditional and modern medicines.
- Researchers collected K. galanga L. germplasm from southern states of Kerala and Karnataka and evaluated the samples for essential oil content and oil composition.
- They analyzed volatile oil isolated from rhizomes of K. galanga L. by hydrodistillation using gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS).
- The researchers identified 38 aroma compounds in the rhizome oil representing 96.4 percent to 98.9 percent of total oil. The two major compounds identified were trans-ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate (28.4–70.0 percent) and trans-ethyl cinnamate (11.5–26.6 percent), which constituted 50.3 percent to 84.8 percent of total oil.
- Other important chemical compounds present were:
- Delta-3-carene (0.1–6.5 percent)
- 1,8-cineole (0.2–5.2 percent)
- Borneol (1.0–2.4 percent)
- Pentadecane (6.0–16.5 percent)
- The researchers found that trans-ethyl-p-methoxycinnamate and trans-ethyl cinnamate were the most vital constituents responsible for most of the pharmacological properties of K. galanga.
Based on these findings, the researchers conclude that the promising accessions identified could be exploited for large-scale cultivation of K. galanga for obtaining higher yields of pharmacologically important constituents.
Journal Reference:
Raina AP, Abraham Z. CHEMICAL PROFILING OF ESSENTIAL OIL OF KAEMPFERIA GALANGA L. GERMPLASM FROM INDIA. Journal of Essential Oil Research. 2015;28(1):29–34. DOI: 10.1080/10412905.2015.1077165
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, aromatic ginger, essential oil, galangal, herbal medicine, Herbs, medicinal plants, natural cures, natural medicine, remedies, traditional medicine