Efficacy of TCM studied for treating colorectal cancer
05/29/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
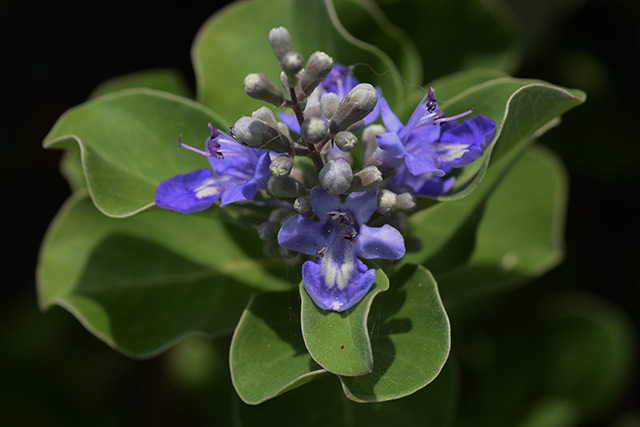

In this study, researchers from Andong National University in South Korea investigated the inhibitory effect of Victis Fructus (VF), the dried fruit of the plant Vitex rotundifolia (beach vitex), on the down-regulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4, which are proteins associated with cancer cell proliferation. Their results, which explained the molecular mechanism behind this inhibition of cell proliferation, were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
- VF is used as a traditional medicine for treating inflammation, headache, migraine, chronic bronchitis, eye pain, and gastrointestinal infections.
- VF has antiproliferative effects against various cancer cells, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancer cells, according to studies.
- The molecular mechanisms by which VF inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells have not been elucidated in detail.
- The researchers observed the following:
- VF suppressed the proliferation of human colorectal cancer cell lines such as HCT116 and SW480.
- VF decreased cyclin D1 and CDK4 in both protein and mRNA levels.
- The protein levels of cyclin D1 and CDK4 were decreased by VF at an earlier time than the change of mRNA levels.
- VF suppressed the expression of cyclin D1 and CDK4 via proteasomal degradation.
- In cyclin D1 and CDK4 degradation, Thr286 phosphorylation of cyclin D1 played a pivotal role in VF-mediated cyclin D1 degradation.
- Experiments with several kinase inhibitors suggested that VF-mediated degradation of cyclin D1 may be dependent on GSK3B.
- VF-mediated degradation of CDK4 was dependent on ERK1/2, p38 and GSK3B.
- In the transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4, VF inhibited Wnt activation associated with cyclin D1 transcriptional regulation through TCF4 down-regulation.
- VF treatment down-regulated c-myc expression-associated CDK4 transcriptional regulation.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that VF has the potential to be a candidate for the development of chemoprevention or therapeutic agents for human colorectal cancer.
Journal Reference:
Song HM, Park GH, Park SB, Kim HS, Son HJ, Um Y, Jeong JB. VITEX ROTUNDIFOLIA FRUIT SUPPRESSES THE PROLIFERATION OF HUMAN COLORECTAL CANCER CELLS THROUGH DOWN-REGULATION OF CYCLIN D1 AND CDK4 VIA PROTEASOMAL-DEPENDENT DEGRADATION AND TRANSCRIPTIONAL INHIBITION. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2018;46(01):191–207. DOI: 10.1142/s0192415x18500118
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anticancer, Beach vitex, cancer cures, chemoprevention, Colorectal Cancer, disease treatments, dried fruit, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, pain relief, prevention, remedies, research, TCM, therapeutic agents, traditional Chinese medicine, Victis Fructus, Vitex rotundifolia