Baicalein found to reduce the viability of ovarian cancer cells and induce autophagy
06/13/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
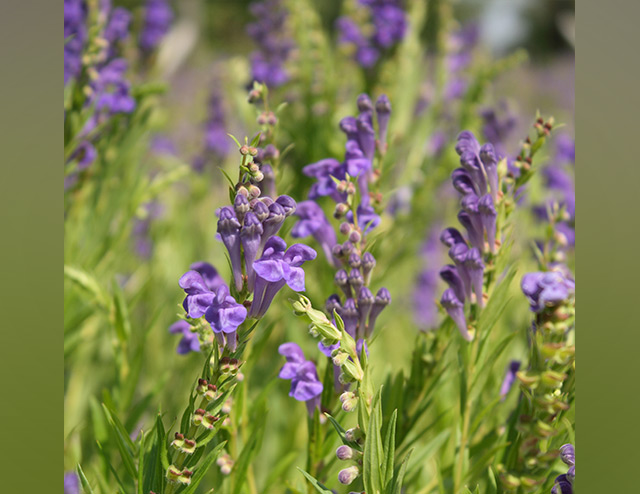

In this study, researchers from the University of Macau investigated the bioactivity of baicalein (BA) isolated from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis or Chinese skullcap against ovarian cancer cells. The results of their study were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
- BA is one of the major bioactive compounds present in the root of Chinese skullcap.
- BA exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities.
- The researchers found that BA has the ability to reduce the cell viability of ovarian cancer cells and induce autophagy.
- They also found that treatment with BA enhanced microtubule-associated protein light chain 3-II (LC3-II) expression, acidic vesicular organelle, and GFP-LC3 fluorescence dot accumulation.
- BA treatment with chloroquine further reduced cell viability and increased the cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in both HEY and A2780 ovarian cancer cell lines, indicating that BA induces protective autophagy in these cells.
- Knockdown of Beclin 1 by siRNA remarkably decreased BA-induced LC3-II lipidation.
- BA treatment increased the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK, Thr202/Thr204) and AKT (Ser473). It also inhibited ERK activation by the pharmacological inhibitor U0126, while ERK siRNA blocked BA-induced autophagy.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that BA can induce Beclin 1- and ERK-dependent autophagy in ovarian cancer cells, proving its potential as a natural anticancer medicine.
Journal Reference:
Wang YF, Xu YL, Tang ZH, Li T, Zhang LL, Chen X, Lu JH, Leung CH, Ma DL, Qiang WA, Wang YT, Lu JJ. BAICALEIN INDUCES BECLIN 1- AND EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL-REGULATED KINASE-DEPENDENT AUTOPHAGY IN OVARIAN CANCER CELLS. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2017;45(01):123–136. DOI: 10.1142/s0192415x17500094
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antioxidant, autophagy, baicalein, cancer cures, chinese skullcap, disease treatments, flavonoids, herbal medicine, Herbs, medicinal plants, natural cures, natural medicine, Ovarian Cancer, prevention, remedies, research, Scutellaria baicalensis, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine, women's health