Chebulinic acid, a primary component in triphala, demonstrates anti-tumor properties
07/02/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
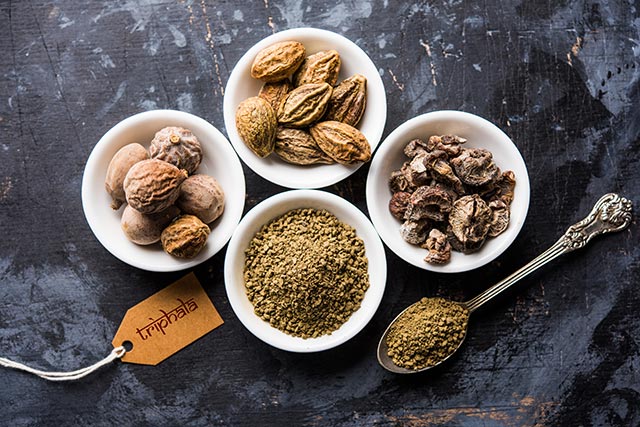

In this study, researchers from China evaluated the anti-proliferative activities of chebulinic acid and chebulagic acid — both of which are found in the Ayurvedic medicine triphala — against cancer cells. The results of their study were published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Triphala is an Ayurvedic rasayana formulation reputed for its antitumor activities.
- Chebulinic acid and chebulagic acid, along with other phenolic acids, are responsible for triphala’s effects.
- The researchers used colorectal carcinoma cell lines with three phenotypes for their in vivo experiments.
- They exposed the cells to several batches of triphala containing different quantities of chebulinic acid and chebulagic acid.
- They also investigated the pro-apoptotic and anti-migratory activities and the probable antitumor mechanisms of the more potent anti-proliferative phytochemical, chebulinic acid.
- They found that chebulinic acid exerts potent anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic, and anti-migratory effects. It is also a key molecule for maintaining the antitumor efficacy of triphala.
- The researchers believe that the antitumor mechanism of chebulinic acid is related to the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways.
Based on their findings, the researchers concluded that chebulinic acid is not only a critical component of the anticancer activities of triphala, but also a promising natural, multi-target and antitumor agent with therapeutic potential.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Wang M, Li Y, Hu X. CHEBULINIC ACID DERIVED FROM TRIPHALA IS A PROMISING ANTITUMOUR AGENT IN HUMAN COLORECTAL CARCINOMA CELL LINES. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 27 December 2018;18(1):342. DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2412-5
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, Amla, anticancer, antitumor, Ayurveda, Ayurvedic medicine, cancer cures, cancer treatment, chebulagic acid, chebulinic acid, chemoprotective, Colorectal Cancer, disease treatments, eye health, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, herbal medicine, Herbs, longevity, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, remedies, research, traditional medicine, triphala, tumor invasion