Could a simple vitamin be an anti-aging tool?
08/13/2019 / By Stephanie Diaz
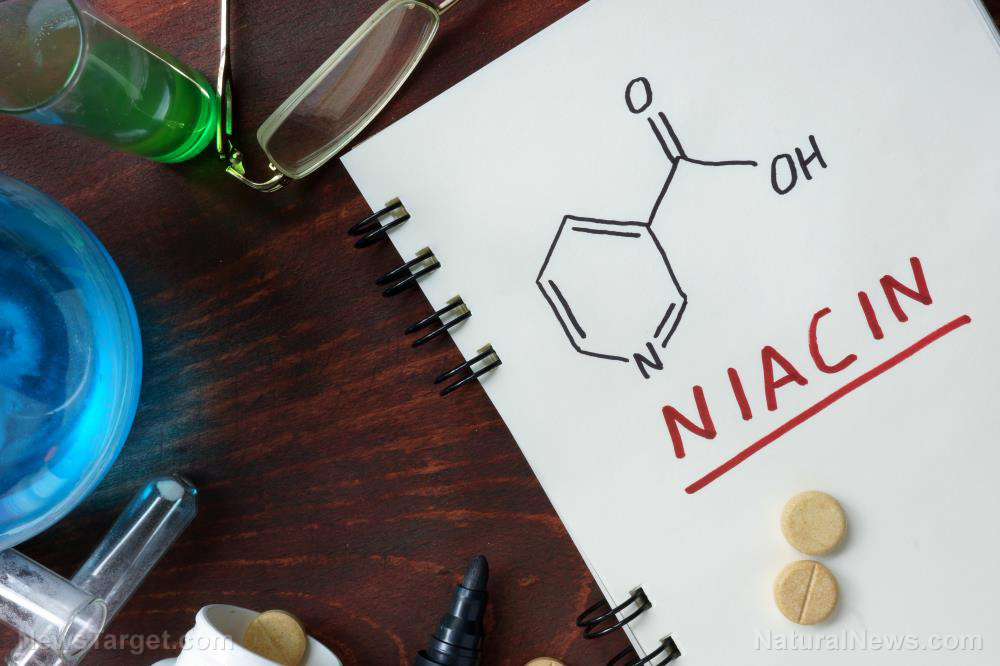

Many factors contribute to the aging process. In particular, oxidative damage is said to be the leading cause of aging. However, scientists may have just found a way to slow down aging. In a research published in the journal Nature Communications, researchers found that niacinamide or vitamin B3 can protect against oxidative damage and delay the onset of aging.
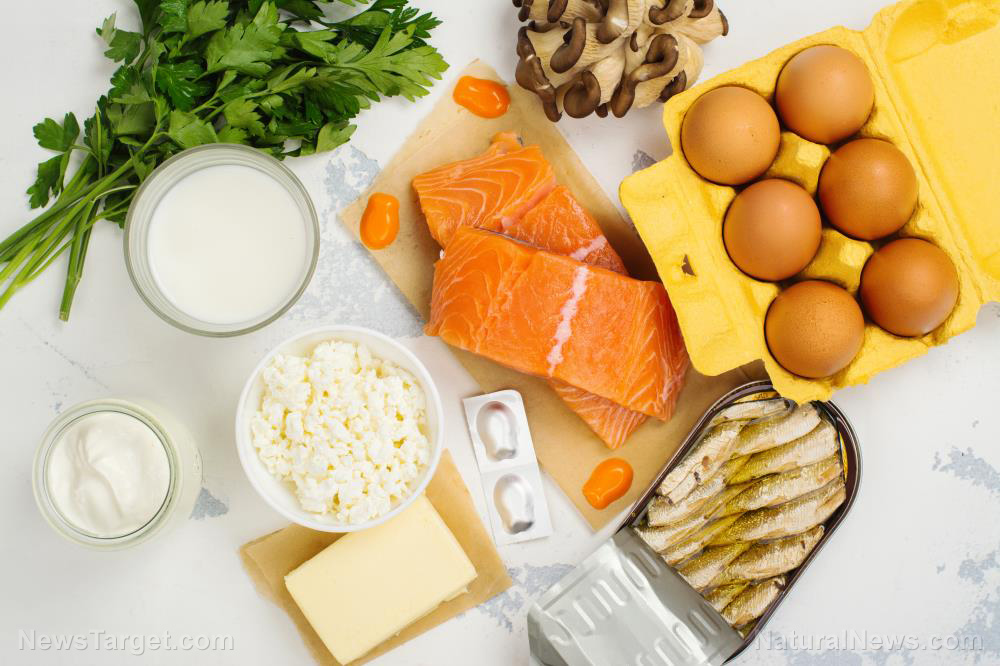
Vitamin B3 or nicotinamide riboside chloride – or simply niacin – is one of the eight B vitamins. It plays a key role in digestive, skin, hair, and nerve health.
Vitamin B3 boosts production of an anti-aging compound
The health benefits of niacin are often attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Research has found that niacin can help boost the production of an enzyme called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
NAD is found in all cells and plays a vital role in metabolic processes. It helps turn nutrients to cellular energy and works with protein to regulate certain biological activities. These biological activities are an essential component for managing oxidative stress. Unfortunately, levels of NAD in the body declines with age.
Researchers from the University of Colorado wanted to find out if supplementing with vitamin B3 could help raise levels of NAD. To investigate, they recruited 30 adults to participate in the study. Researchers asked the participants to take 500 mg of vitamin B3 two times a day and one placebo pill once a day for six weeks. They found that supplementing with vitamin B3 could stimulate NAD production in the body. Their results also revealed that increased vitamin B3 intake could reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. The daily supplementation of vitamin B3 helped regulate blood pressure levels and prevented arterial stiffness.

The researchers highlighted the importance of NAD in the body. “NAD+ is critically involved in just about every metabolic process in our cells,” said Christopher Martens, lead author of the study. He also added, “We believe that by boosting NAD+ back to youthful levels, we can improve physiological function and possibly prevent the risk for age-related diseases.”
More reasons to incorporate vitamin B3 into your daily routine
Aside from slowing down the signs of aging, vitamin B3 can also decrease acne and hyperpigmentation, prevent cancer and diabetes, and manage osteoarthritis. (Related: Vitamin B3 may be the cure for drug-resistant superbug infections.)
- Decrease acne: Research shows that niacinamide contains anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce acne. Topical treatment that contains vitamin B3 can be applied to the affected area. Taking niacinamide supplements is also known to reduce acne.
- Reduce hyperpigmentation: Several early-stage clinical trials reveal that photoaging can be treated using niacinamide. Moreover, many people believe that niacinamide can reduce uneven skin tone caused by hyperpigmentation and melasma.
- Prevent cancer: Research published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that niacinamide was effective at reducing the risk of skin cancers. They asked high-risk participants to take niacinamide treatments for over a year. Their results showed that niacinamide helped the participants reduce their risk of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma by 23 percent. Furthermore, treatment with niacinamide reduced the risk of developing actinic keratosis or pre-cancer.
- Prevent diabetes: There are studies that suggest that niacinamide can prevent and treat early stages of Type 1 diabetes — an insulin-dependent type of diabetes.
- Manage osteoarthritis: People who have osteoarthritis can benefit from niacinamide supplementation . Many studies show that niacinamide helps manage the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Regular intake of this vitamin can improve joint flexibility and reduce inflammation. Moreover, with regular consumption, it may be possible to decrease the use of anti-inflammatory medicines.
Read up on other wonderful skin benefits that you can get from niacin and other vitamins at SupplementsReport.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
acne, aging, aging secrets, anti-aging, anti-aging science, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, b vitamins, diabetes, hyperpigmentation, NAD, niacin, Niacinamide, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, nicotinamide riboside, ostoarthritis, prevention, skin cancer, slow aging, supplements, vitamin B3
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author