Fermented red ginseng relieves side effects of colitis medication
08/26/2019 / By Janine Acero
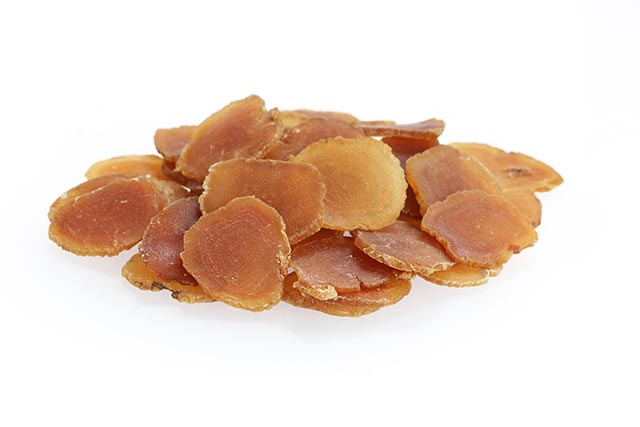

Sometimes the medications that are meant to treat a certain condition can cause side effects that leave your body more vulnerable to sickness. Certain pharmaceutical drugs, for example, cause immunosuppression and colitis. Korean researchers studied the effects of Asian ginseng (red ginseng) on these side effects. Their findings were published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.
The study
Immunosuppression is the partial or complete suppression of immune response. In some cases, it can be induced to help an organ survive after a transplant operation. Colitis is a chronic condition marked by inflammation of the lining of the colon.
For their study, the researchers used steamed roots of Panax ginseng or red ginseng (RG). They obtained water-extracted RG (wRG), 50 percent ethanol-extracted RG (eRG), enzyme-treated eRG (ERG) and probiotic-fermented eRG (FRG) and examined their effects on cyclophosphamide (CP)-induced immunosuppression (CI) or 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis (TC) in mice.
CP has cytotoxic and immunosuppressive properties, and is used as a treatment for malignant and inflammatory conditions. TNBS, on the other hand, is a drug that can induce colitis.
The researchers gave mice RG via oral administration and found that it significantly increased blood IFN-y (interferon gamma) levels. Interferons are a group of proteins released by cells in response to the presence of viruses. Virus-infected cells release interferons to trigger the anti-viral defenses of nearby healthy cells.
The researchers also found that RG increased the tumoricidal (anti-tumor) effects of CI mouse splenic cytotoxic T (Tc) cells and natural killer (NK) cells against YAC-1 cells. YAC-1 cells are T cell lymphomas that are sensitive to the cytotoxic activity of NK cells.

|
Discover how to prevent and reverse heart disease (and other cardio related events) with this free ebook: Written by popular Natural News writer Vicki Batt, this book includes everything you need to know about preventing heart disease, reversing hypertension, and nurturing your cardiac health without medication. Learn More. |
The researchers reported that treatment with FRG increased the differentiation of splenic T cells into type 1 T (Th1) and regulatory T (Treg) cells in vitro. Moreover, both FRG and wRG significantly increased Th1 cell differentiation. Th1 cells are immune cells that release IFN-y in response to the presence of pathogens.
The researchers found that all treatments with RG, except wRG, increased Treg cell differentiation. However, only wRG increased IL-6 and IL-17 expression in the colon of CI mice. Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines — cell signalling molecules — secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes). Other types of cytokines include interferons and growth factors.
RG extracts also inhibited TNF-a (tumor necrosis factor alpha) expression and increased IL-10 expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated primary macrophages in vitro. TNF-a is a cytokine involved in systemic inflammation.
FRG suppressed TNBS-induced colon shortening, NF-kB activation and TNF-a and IL-17 expression. On the other hand, it also increased IL-10 expression, indicating that RG can alleviate colitis in TC mice.
The researchers concluded that, of the four extracts they used, FRG or probiotic-fermented red ginseng extract has the most potent immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties allowed it to inhibit macrophage activation and regulate Th1 and Treg cell differentiation to alleviate immunosuppression and inflammation. (Related: A natural treatment for colitis: Red ginseng powder fermented with probiotics.)
American ginseng
Other species of ginseng can also serve as potent treatments for other forms of colitis. For instance, American ginseng (P. quinquefolius) alleviates ulcerative colitis, a chronic inflammatory condition associated with high colon cancer risk.
In a 2008 study, researchers reported that American ginseng can suppress inflammation and DNA damage associated with ulcerative colitis. To investigate its effects, they gave mice American ginseng extracts after the onset of colitis. They found that the extract inhibited leukocyte activation and subsequent epithelial cell DNA damage both in vitro and in vivo. Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that American ginseng can be used for the prevention and treatment of ulcerative colitis.
Visit Herbs.news for more studies on the medicinal properties of Asian and American ginseng.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, American ginseng, anti-inflammatory, colitis, colitis treatments, harmful medicine, herbal medicine, Herbs, immune cells, immune system, immunomodulatory, immunosuppression, inflammation, natural cures, natural medicine, Panax ginseng, prevention, red ginseng, remedies, research, side effects, ulcerative colitis