Moxibustion may improve IBS by stimulating gut microbiota
09/03/2019 / By Stephanie Diaz
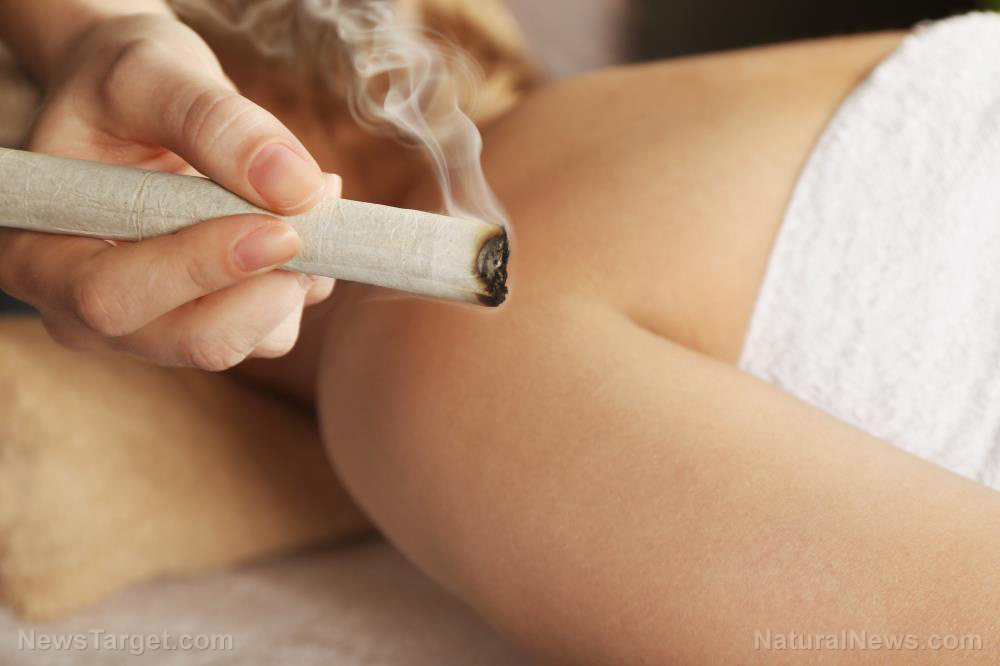

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder; it affects up to 20 percent of the global population at any given time. In a study published in Chinese Medicine, researchers from the Shanghai University of Traditional Medicine and Indiana University School of Medicine suggested using a form of heat therapy called moxibustion to treat IBS.
Moxibustion promotes a healthy gut microflora
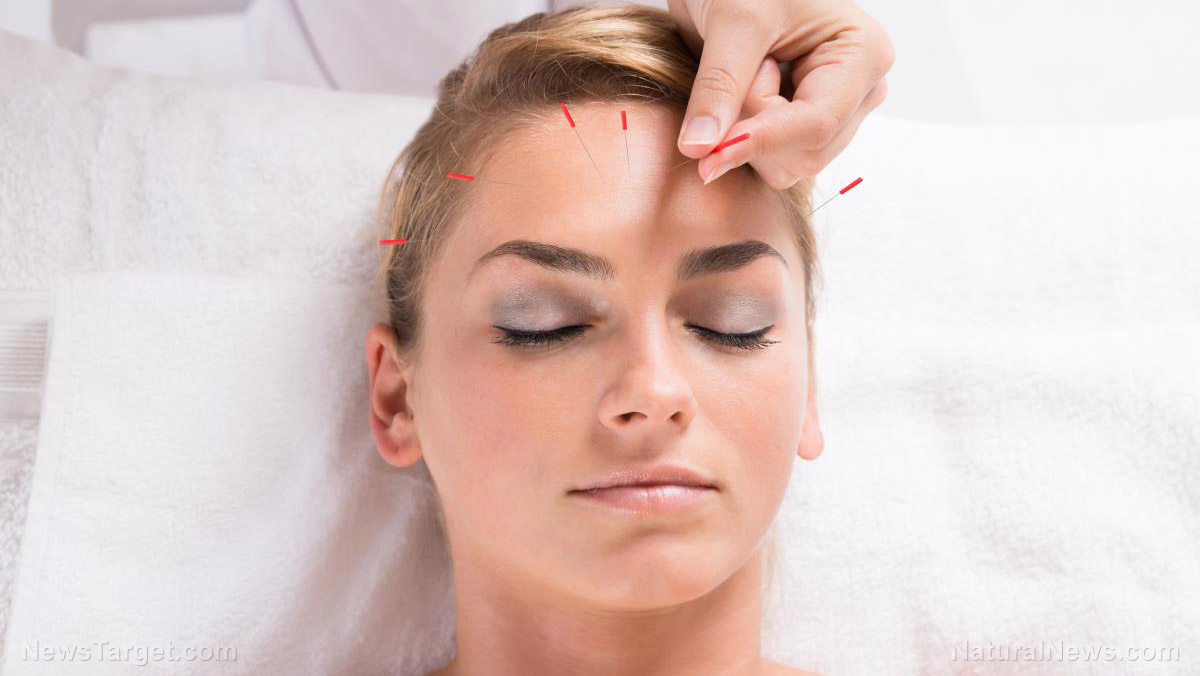
Moxibustion is a procedure used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat chronic conditions and improve a person’s overall well-being. Dried mugwort leaves are burned to generate heat near the surface of the skin to stimulate specific points and promote repair.
TCM practitioners believe that the heat generated by burning mugwort leaves increases the flow of vital energy, commonly known as “chi,” in the different parts of the body by going through specific pathways called meridians. The increase in chi “unblocks” certain points in the body, promoting healing.
There are two types of moxibustion treatment: direct and indirect. In direct moxibustion, burning moxa is placed directly on the surface of the skin. Indirect treatment, meanwhile, uses burning moxa directed one to two inches away from the skin. Other forms place it near the tip of an acupuncture needle that is already set in an acupoint. Today, indirect moxibustion is widely used as directly applying moxa to the skin can potentially burn it and cause pain and scarring.
In their study, researchers studied the effect of moxibustion on rats with IBS for seven days. They found that the treatment decreased the abdominal sensitivity of rats, making them less susceptible to the effects of IBS. They also found that moxibustion improved the balance of good and bad bacteria in the gut. This balance promotes gut health and decreases the chance of acquiring IBS. (Related: Moxibustion is an effective alternative cancer treatment, according to study.)

|
Discover how to prevent and reverse heart disease (and other cardio related events) with this free ebook: Written by popular Natural News writer Vicki Batt, this book includes everything you need to know about preventing heart disease, reversing hypertension, and nurturing your cardiac health without medication. Learn More. |
“Our findings suggest that moxibustion treats IBS by modulating the gut microbiota,” they concluded in their report. “We demonstrate that moxibustion could potentially be used to regulate gut microbiota imbalances and therefore, to treat patients with IBS.”
Other health benefits of moxibustion treatment
Moxibustion is great for improving conditions other than IBS.
- It helps with pain relief. The heat released by the leaves increases the flow of chi and invigorates the body. It also stimulates the nerves to release hormones that help with pain management.
- It relieves hot flashes. Women nearing menopause experience hot flashes, a condition which induces intense warmth in the face, neck, and chest area. According to a study published in Menopause, moxibustion was effective in reducing the duration and severity of menopausal hot flashes.
- It boosts the immune system. Ancient Japanese and Chinese medicine recommended daily moxibustion treatment on an acupuncture point called Stomach 36, which is found just below the kneecap near the calves. Practitioners believe that moxibustion treatment in this area revitalizes the immune system. Moreover, stimulation in Stomach 36 promotes vitality and longevity.
- It may help correct a breech during pregnancy. Moxibustion is also known for correcting a breech, where the legs or buttocks of a fetus is near the cervix. For this procedure, indirect moxibustion is done on a point called bladder 67, which is just on the outer edge of the pinkie toe.
To know more about moxibustion and acupuncture, visit ChineseMedicine.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: acupuncture, alternative medicine, bacteria, cardiovascular health, Chinese medicine, diarrhea, digestion, disease treatments, food cures, gastrointestinal health, gut health, heart health, herbal medicine, Herbs, IBS, immune system, irritable bowel syndrome, microbiota, microflora, moxibustion, natural cures, natural medicine, pain relief, prevention, remedies, research, TCM, traditional medicine