Vitamin D deficiency the likely cause for a rise in rickets cases in children
09/10/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

Recently, a rise in the number of rickets cases, especially among children from low-income families, has been reported. Rickets is a skeletal disorder associated with calcium, phosphate, and vitamin D deficiency. While poor nutrition may be a possible reason for the increase in rickets cases, a new study reveals that even some supplements cannot provide children sufficient amounts of vitamin D.
In their short report, researchers from the University of Southampton in the U.K. studied several children’s multivitamins and vitamin D supplements to determine how much of the nutrient they contained. The results of their investigation were published in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood.
- Public Health England, an executive agency under the Department of Health and Social Care in the U.K., recommends a daily intake of 400 IU of vitamin D for children over one year of age.
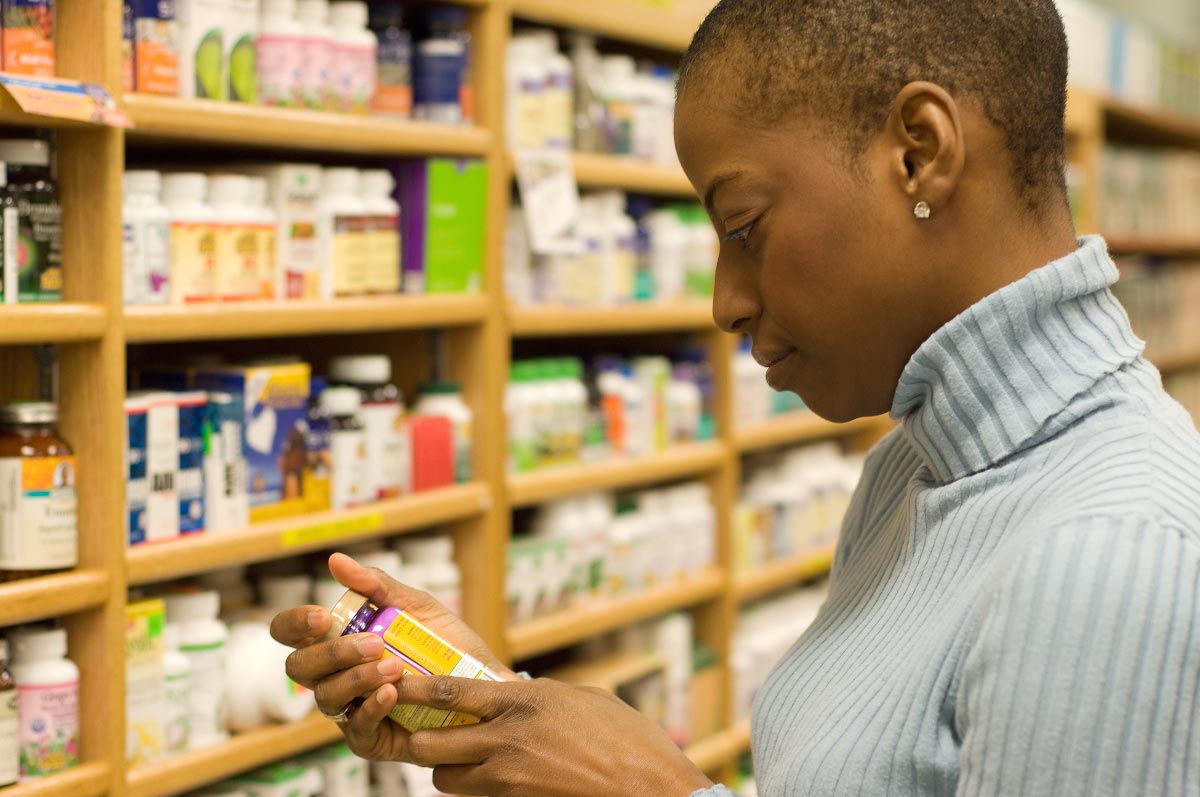
- To determine whether commercially available supplements are enough, the researchers surveyed 67 multivitamins and vitamin D supplements for children younger than 12 years old sold in nine UK supermarkets. They also surveyed the health supplement retailers.
- The researchers determined the vitamin D content of the supplements using data from the manufacturers’ websites and the information provided in the products’ packaging.
- They reported that the vitamin D content of the multivitamins ranged from 0 to 800 IU. Only 25 to 36 percent of the samples could provide more than 400 IU vitamin D per day.
- Meanwhile, supplements that contained only vitamin D or were simply labeled “for healthy bones” had higher vitamin D content than the multivitamins. 57 to 67 percent could provide more than 400 IU vitamin D per day.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that a number of supplements can supply children the recommended 400 IU of vitamin D per day. Because of this, clinicians should take caution when recommending vitamin D supplements and advise parents to choose a product that could meet the requirement.
Moon RJ, Curtis EM, Cooper C, Davies JH, Harvey NC. VITAMIN D SUPPLEMENTATION: ARE MULTIVITAMINS SUFFICIENT? Archives of Disease in Childhood. 25 February 2019. DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2018-316339
Tagged Under: calcium deficiency, children's health, health supplements, multivitamins, nutrients, phosphate deficiency, poor nutrition, research, rickets, science, skeletal disorder, vitamin D, vitamin D deficiency, vitamin D supplements