Antibacterial potential of ginger against nosocomical infections
09/12/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

Researchers from the Botswana International University of Science and Technology evaluated the anti-microbial potential of ginger root extracts and compared their zones of inhibition against nosocomial pathogens with those of synthetic antibiotics. The results of their study were published in the Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.
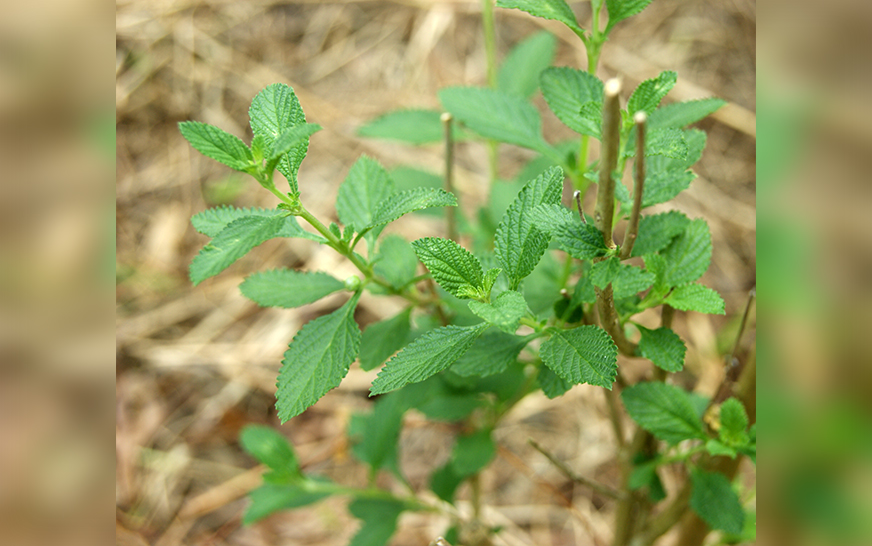
- Ginger (Zingiber officinale) is a well-known medicinal plant and culinary ingredient that has been used for decades.
- To determine its anti-microbial potential, the researchers tested ginger root extracts on five bacterial pathogens, namely, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. They used the Kirby-Bayer agar diffusion method to compare the extracts’ zones of inhibition with those of known antibiotics.
- The researchers reported that the ginger root extracts exhibited higher antimicrobial activity than the antibiotics.
- They also reported that of the five pathogens, S. aureus was the least resistant to antibiotics, while the other four showed strong resistance.
- Meanwhile, at a concentration of 20 milligrams per milliliter (mg/ml), the ginger extracts proved effective against E. coli. However, it was ineffective against S. aureus at a concentration of 75 mg/ml.
- Using phytochemical screening, the researchers confirmed the presence of secondary plant metabolites in the extracts. These metabolites included saponins, tannin, flavonoids, glycoside, terpenoids, and alkaloids. Some of these phytonutrients are responsible for the ginger extracts’ antibacterial activity.
- Because of their potency, these compounds can be used independently or in combination with antibiotics to create more efficient antimicrobial drugs.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that their study contributes to ongoing research about alternative treatments for nosocomial infections. This could also open the door for researchers to be involved in the creation of antibiotics toward which nosocomial pathogens have no resistance.
Journal Reference:
Hannaty A, Goabaone G. ANTIBACTERIAL POTENTIAL OF EXTRACTS OF THE ROOTS OF ZINGIBER OFFICINALE AGAINST BACTERIAL STRAINS COMMONLY ASSOCIATED WITH NOSOCOMIAL INFECTIONS. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research. 25 January 2019;13(2):41–46. DOI: 10.5897/jmpr2018.6685
Tagged Under: alkaloids, alternative medicine, Antibiotics, Antimicrobial, bacteria, clean food, Enterobacter aerogenes, Escherichia coli, flavonoids, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, ginger, glycoside, herbal medicine, Herbs, hospital infections, immune system, Klebsiella pneumoniae, natural antibiotics, natural cures, natural ingredients, natural medicine, nosocomial infections, nosocomial pathogens, phytonutrients, plant medicine, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, remedies, research, saponins, Staphylococcus aureus, tannin, terpenoids, Zingiber officinale