Acanthophora spicifera found to have anti-coagulant and anti-platelet effects
09/16/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
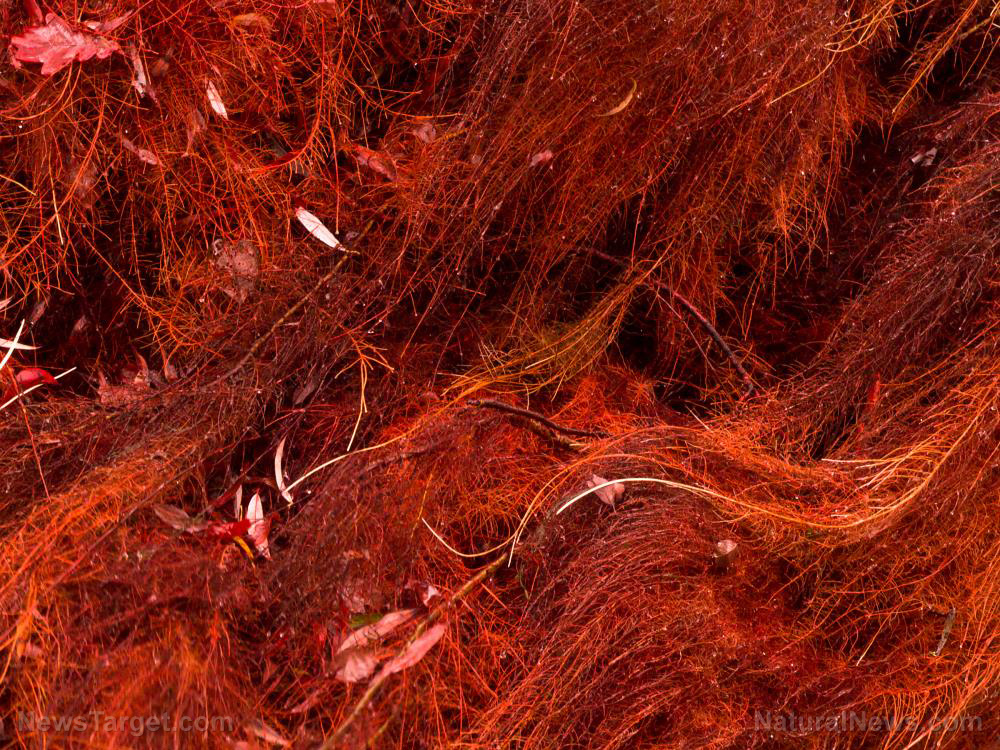

Researchers from Federal Fluminense University in Brazil evaluated the anti-coagulant and anti-platelet effects of extracts from Acanthophora spicifera and some commercial products, such as biotin, myristic acid, cholesterol, beta-carotene, and vitamin B12. The results of their study were published in the Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.
- Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death and morbidity around the world.
- Thrombi or blood clots, which can cause a heart attack or stroke, are formed when both platelet aggregation and coagulation are dysregulated.
- Due to the limitations and side effects of conventional anti-thrombotic drugs, researchers have begun exploring alternative treatments.
- In line with this, the researchers investigated the potential of extracts obtained from a Brazilian alga to prevent blood clotting.
- They prepared multiple extracts using different solvents and evaluated them in terms of prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen coagulation, and thrombin time — measures routinely used for clinical trials and on platelet aggregation.
- The researchers reported that all of the A. spicifera extracts and commercial products they tested successfully inhibited plasma coagulation and collagen- or ADP-induced platelet aggregation.
- The extracts also inhibited the enzymatic activity of thrombin and proved to be non-cytotoxic, as evidenced by the absence of platelet or red blood cell lysis.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that the commercial products they tested and the A. spicifera extracts have therapeutic potential and can be used to develop a new class of anti-hemostatic drugs.
Journal Reference:
Vivian RDS, Laura DAM, Ana CRDS, Kelly KGP, Caio CRN, Diana NC, Valeria LT, Andre LF. EXPLORING THE ANTICOAGULANT AND ANTIPLATELET EFFECT OF THE EXTRACTS OF THE RED MARINE ALGA ACANTHOPHORA SPICIFERA. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research. 25 January 2019;13(2):31–40. DOI: 10.5897/jmpr2018.6718
Tagged Under: Acanthophora spicifera, algae, alternative medicine, anti-coagulant, anti-hemostatic, anti-platelet, Blood clots, blood coagulation, disease treatments, heart attack, heart disease, heart health, natural cures, natural medicine, platelet aggregation, prevention, prothrombin, research, reverse heart disease, stroke, thrombin