Leaf extracts from Indian coleus can be used as a potent novel drug against serious ailments and disorders
04/13/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

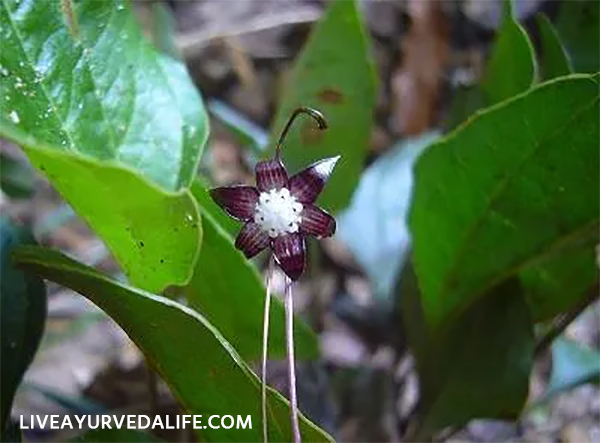
Coleus forskohlii, also known by the names forskohlii or Indian coleus, is a medicinal plant that’s native to India. Since ancient times, this tropical perennial plant — like other members of the genus Coleus — has been used in traditional medicine to treat various disorders, such as those that affect the cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems.
In a recent study published in The Journal of Phytopharmacology, researchers at Osmania University in India screened leaf extracts from C. forskohlii to determine their phytochemical content. They found that Indian coleus extracts are rich in bioactive compounds that possess a variety of medicinal properties. The researchers believe that these phytochemicals can be developed into novel drugs that can be used for the treatment of serious health conditions.
Indian coleus can be used to develop new natural-based medicines
Indian coleus is a tropical perennial plant that is extensively cultivated in the southern and western parts of India. Even in China, it is widely used as a natural remedy for common digestive issues.
According to studies, Indian coleus can help lower blood pressure by dilating the blood vessels. It is also considered a traditional cure for cutaneous infections, such as scabies, guinea worm, eczema and herpes-related skin problems.
To identify the medicinal compounds present in Indian coleus, the researchers used various solvents, such as water, methanol, chloroform, ethyl acetate and acetone, to obtain Indian coleus leaf extracts.
They found that, besides plant carbohydrates and lipids, Indian coleus is rich in the following compounds, which are all associated with a variety of medicinal properties:
- Glycosides — These compounds can be found in many useful herbs and are used as active ingredients of some modern medicines. For instance, the foxglove herb (Digitalis purpurea) produces a class of compounds known cardiac glycosides. These glycosides are used for the treatment of heart failure and irregular heartbeats.
- Tannins — An organic compound widely distributed in plants, tannins are said to be responsible for the color, astringency and some of the flavor in green tea. Tannins are used to treat various complaints, such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis, hemorrhoids, and skin eruptions. Tannins have also been used to relieve diarrhea and intestinal bleeding.
- Flavonoids — One of the better-known classes of beneficial phytonutrients, flavonoids have demonstrated antioxidant, anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer and anti-aging properties in numerous studies.
- Triterpenoids — Found in popular herbs like Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng), Indian frankincense (Boswellia serrata) and reishi mushroom (Ganoderma lucidum), triterpenoids are said to have anti-in?ammatory, hepatoprotective, analgesic, anti-microbial, anti-fungal, virostatic, immunomodulatory and tonic effects.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that Indian coleus is an excellent source of phytochemicals that can be developed into novel medicines for various ailments.
The medicinal uses of Indian coleus
Indian coleus is traditionally used as a natural medicine for heart disorders, such as chest pain and hypertension, and respiratory disorders like asthma. Forskolin, an active compound isolated from the roots of Indian coleus, is also credited with enhancing lipolysis or the degradation of fat. This activity of forskolin promotes weight loss and the reduction of body fat without any loss of muscle mass.
Here are some conditions for which Indian coleus is used as treatment:
- Asthma
- Dry eyes
- Erectile dysfunction
- Idiopathic congestive cardiomyopathy
- Glaucoma
- Obesity
- Allergies
- Blood clots
- Cancer
- Insomnia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Menstrual pains
- Seizures
- Urinary tract infections
Indian coleus is a potent herb with a wide range of medicinal applications. However, it can interact with other medications, such as anti-hypertensive drugs and anticoagulants. To avoid unwanted side effects due to these interactions, consult with a natural health practitioner before using this herb for treatment.
Sources include:
PhytoPharmaJournal.com [PDF]
Tagged Under: Coleus forskohlii, digestion, flavonoids, glycosides, herbal medicine, Herbs, Indian coleus, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients, plant medicine, remedies, research, skin infections, tannins, triterpenoids