Study reveals the antimicrobial and antiplasmodial effects of Canthium subcordatum
06/23/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

In this study, researchers from Cameroon and Germany investigated the anti-plasmodial and antimicrobial activities of Canthium subcordatum extracts and isolated compounds. Their findings were published in The Journal of Phytopharmacology.
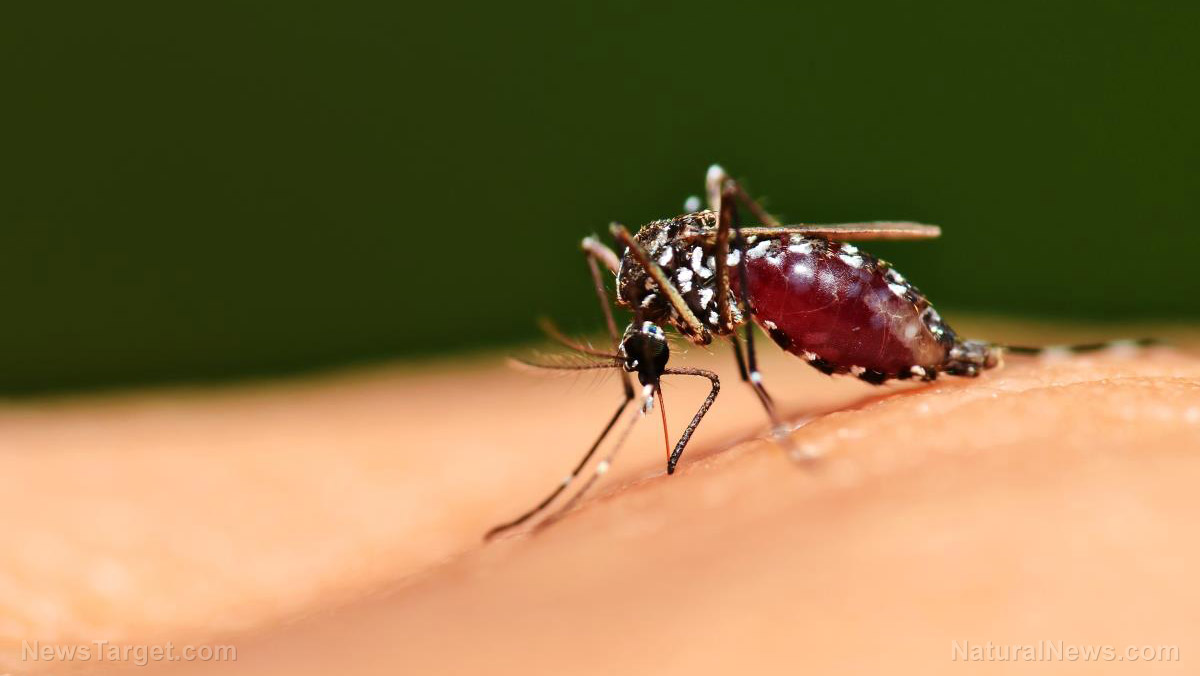
- Protozoan parasites from the genus Plasmodium are known to cause malaria, one of the most widely known infectious diseases on the planet.
- P. falciparum is the species responsible for nearly all of the severe malaria cases and malaria-related deaths reported worldwide.
- Medicinal plants have always been considered excellent sources of antimalarial agents, such as quinine and artemisinin.
- The genus Canthium consists of medicinal plants that belong to the madder (Rubiaceae) family.
- It is a poorly defined genus with about 50 species, including C. subcordatum, which is found in Africa and Asia.
- The stem bark, leaves and roots of the plant are used in folk medicine to treat diabetes, fever, inflammation, cardiovascular disease and malaria.
- In Cameroon, traditional healers also use C. subcordatum to treat stomach disorders.
- Phytochemical analysis of its stem bark revealed that it contains the following compounds:
- B-sitosterol
- Ursolic acid
- Cerbinal
- Quinovic acid
- Cerberinic acid
- 3-O-B-D-glucopyranosyl quinovic acid
- 3-O-B-D-glucopyranosyl oleanolic acid
- Clemahexapetoside B
- This is the first time cerbinal, cerberinic acid and clemahexapetoside B were isolated from a Canthium plant.
- Upon testing the fractions and isolates for their antiplasmodial activity, the researchers found that only the methanol fraction inhibited the growth of P. falciparum with an IC50 of 3.044 mcg/mL.
- Of the isolates, quinovic acid and cerberinic acid showed the highest activity against eight bacterial and fungal strains, with inhibition diameter zones equal to or above 12 mm and minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) equal to or lower than 39 mcg/mL.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that C. subcordatum is a potent antimalarial and antimicrobial agent.
Journal Reference:
Awantu AF, Fotsing FYS, Bankeu KJJ, Lenta NB, Tsouh FPV, BoyomFF, Assob NJC, Tsamo E, Sewald N. ANTIPLASMODIAL AND ANTIMICROBIAL POTENTIAL OF CANTHIUM SUBCORDATUM EXTRACTS AND ISOLATES. The Journal of Phytopharmacology. 2019;8(2):52-56.
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antimalarial, Antimicrobial, antiplasmodial, Canthium subcordatum, disease treatments, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients, plant medicine, research