PARASITES called Kissing Bugs spreading DEADLY CHAGAS DISEASE in Florida; 280,000 suspected of being infected
07/16/2025 / By S.D. Wells
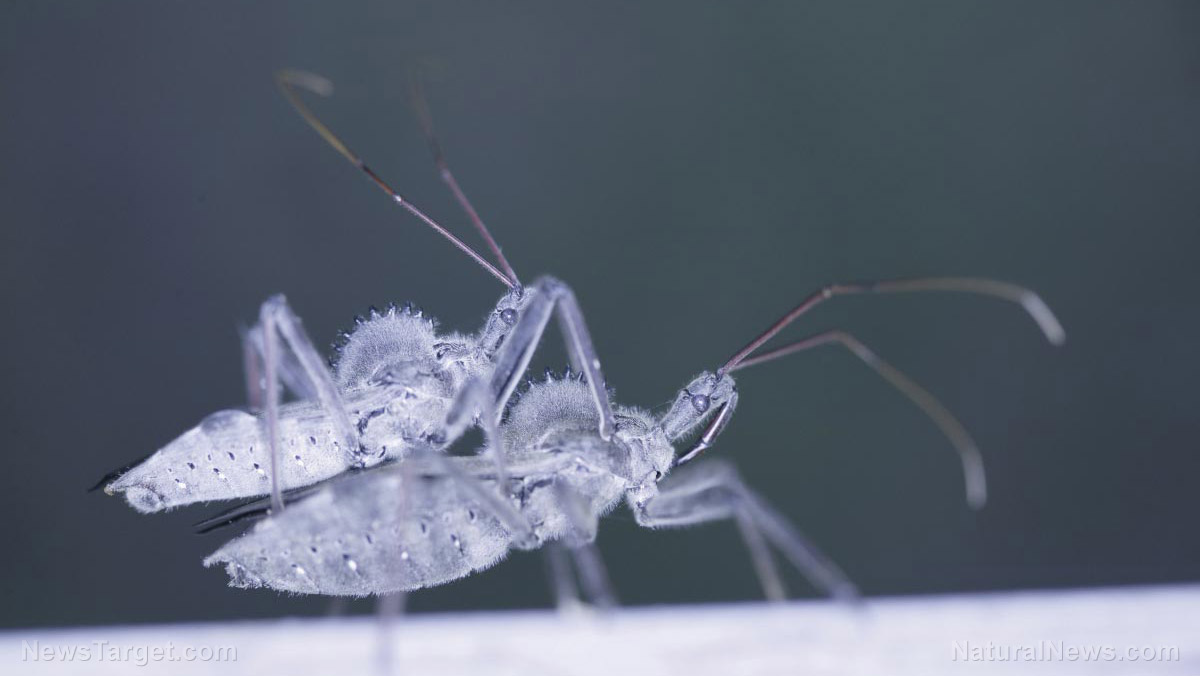

Health experts are raising alarms over a growing threat in the southeastern United States: parasitic bugs that feed on humans and transmit a potentially deadly disease. A decade-long study conducted in Florida and Texas has revealed that Trypanosoma cruzi — a parasite spread by blood-sucking triatomine bugs, commonly known as “kissing bugs” — is infecting both humans and animals, often without their knowledge.
- Kissing bugs in the southeastern U.S. are spreading Chagas disease, a potentially deadly parasitic infection caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, which can lead to heart failure, blood clots and digestive system damage if left untreated.
- Researchers found that over one-third of kissing bugs collected in Florida were inside homes, with one in three carrying the parasite and feeding mostly on humans and pets, particularly in areas where housing encroaches on undeveloped land.
- Chagas disease often goes undetected for decades, earning it the nickname “silent killer.” Though many infected people show no early symptoms, chronic stages can include serious cardiovascular and digestive complications.
- Experts advise preventive steps like habitat management, such as keeping woodpiles away from homes and pet sleeping areas, sealing cracks in walls, and avoiding conditions that attract bugs, rather than relying solely on pesticides.
Experts warn parasites are ‘feeding on humans’ in the U.S. and transmitting deadly disease
Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas disease, a condition known for its silent progression and devastating long-term effects. It is currently estimated that approximately 280,000 people in the U.S. are infected with the parasite, many of them unaware due to the disease’s subtle symptoms in its early stages. If untreated, Chagas disease can persist in the body for decades and eventually cause severe health issues such as heart failure, blood clots, digestive complications and even death.
Researchers collected 300 kissing bugs from 23 counties in Florida, finding that over one-third were found inside homes. One in three tested bugs carried the T. cruzi parasite, and infections were detected in more than half of the surveyed counties. The bugs are thought to be entering human living spaces as urban development encroaches upon their natural habitats.
Dr. Norman L. Beatty, an infectious disease physician at the University of Florida and co-author of the study, emphasized the seriousness of the findings: “We have a vector in our state that is harboring a parasite, invading homes, and feeding on humans and our pets.”
Kissing bugs, which range in size from half an inch to over an inch long, are nocturnal predators that hide in dark areas of homes during the day — such as ceilings and wall cracks — and feed on blood at night. They transmit Chagas disease when their infected feces come into contact with human or animal mucous membranes or open wounds, either through scratching or accidental ingestion.
The research, published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, also included analysis of the bugs’ stomach contents. The study found that kissing bugs collected from inside homes had mostly fed on humans, while those outside fed on other mammals, reptiles and amphibians.
As Florida’s population grows and housing expands into undeveloped areas, the likelihood of humans and pets encountering these bugs increases. Dr. Samantha Wisely, a co-author of the study, describes this as a “peri-urban” phenomenon, where suburban expansion overlaps with the bugs’ natural environment, increasing the risk of disease transmission.
Although many people with Chagas disease are asymptomatic in the early stages, symptoms can include fever, fatigue, body aches, rash, and loss of appetite. In the chronic stage, complications such as heart rhythm disorders and digestive issues become more serious.
Experts urge residents, especially in the 29 states where kissing bugs have been detected, to minimize risks by removing woodpiles from near homes and pet sleeping areas, sealing home entry points, and practicing general habitat management to discourage the bugs’ presence. As Dr. Wisely notes, stopping the spread of Chagas isn’t just about chemical solutions — behavioral and environmental changes are essential.
Check out wormwood and food-grade diatomaceous earth for killing internal parasites. Tune your internet dial to NaturalMedicine.news for more tips on how to use natural remedies for preventative medicine and for healing, even from parasites, instead of succumbing to Big Pharma products that cause, spread, and exacerbate disease and disorder.
Sources for this article include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
Chagas disease, chaos, discoveries, Florida, health science, infections, kissing bugs, national security, outbreak, panic, parasites, Plague, real investigations, research, Tropical diseases, Trypanosoma cruzi, Wormwood
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author