Scratch that: Now they’re saying Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) has an R0 as high as 7.05
02/19/2020 / By Ethan Huff
The reproduction rate (R0) of the Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) – meaning the number of other people that one infected person could potentially spread it to – has been steadily rising over the past several months. Early on, it was in the 1.0-2.0 range. Then, it changed to as high as 6.6. Now, the latest science says we’ve breached 7.05.
What this means is that one infected person could spread the Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) to seven other people, who could then each spread it to seven other people themselves. In other words, one infected person infects seven other people, who then collectively infect 49 other people, who then infect 343 other people, who then infect 2,401 people, and on and on it goes.
The R0 figure is important because it’s a measure of how exponentially a virus can begin to spread. A lower R0 basically means that a virus isn’t going to spread out of control, while a higher R0 suggests that everyone needs to get prepared for a major global pandemic – and the latter seems to be where the Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) is headed.
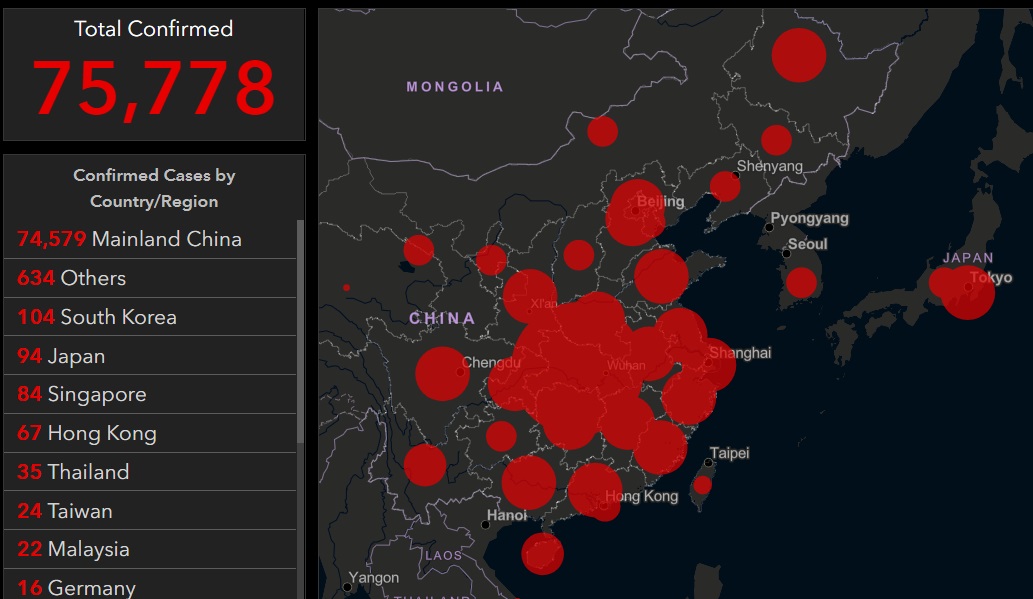
“Since the first cluster of cases was identified in Wuhani City, China, in December, 2019, 2019-nCoV has rapidly spread across China as well as caused multiple introductions in 25 countries as of February, 2020,” a new paper published in the journal medRxiv explains.
“Despite the scarcity of publicly available data, scientists around the world have made strides in estimating the magnitude of the epidemic, the basic reproduction number, and transmission patterns,” it adds. “Recently more evidence suggests that a substantial fraction of the infected individuals with the novel coronavirus show little if any symptoms, which suggest the need to reassess the transmission potential of emerging disease.”
By reconstructing the underlying transmission dynamics of the Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19), the authors came up with a more accurate R0 of 7.05. However, they also contend that the “enhanced public health intervention” imposed by communist China after January 23 helped to bring that R0 down to around 3.24, along with a nearly 10 percent infection rate in Wuhan.
Listen below as Mike Adams, the Health Ranger, explains how communist China has been manipulating the numbers to make it seem like there are far fewer Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) infections than there actually are:
Any R0 above zero means the infection rate is likely to continue increasing
So, what does this all mean in terms of Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) risk in other countries like the United States? It’s difficult to say as health authorities are still grappling with new cases that continue to emerge on airplanes, cruise ships, and even in pockets of the world where there was no known recent travel to Wuhan.
Even a reduced R0 of 3.24, according to this study, is still higher than what the World Health Organization (WHO) initially estimated by putting it at 1.4-2.5. On average, we now know, the R0 is right around 3.28 for the Wuhan coronavirus, making it still a very deadly threat even if it doesn’t persist at 7.05.
“For R0 greater than one the number infected is likely to increase, and for R0 less than one transmission is likely to die out,” reports SciNews, which also covered another similar study that found the R0 for the Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) to be higher than WHO estimates.
“When looking at the development of the CoVid-19 epidemic, reality seems to correspond well to or even exceed the highest epidemic growth in our calculations,” says Professor Rocklöv, one of the authors of this other study.
More breaking news about the Wuhan coronavirus (CoVid-19) is available at Pandemic.news.
Also, be sure to check out the H.R. Report channel at Brighteon.com.
Sources for this article include:
Tagged Under: coronavirus, covid-19, exponential, global emergency, infection, infections, novel coronavirus, outbreak, pandemic, R0, transmission, virus, Wuhan coronavirus