Cudrania tricuspidata extract found to have protective effects against oxidative stress-induced liver injury
02/21/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
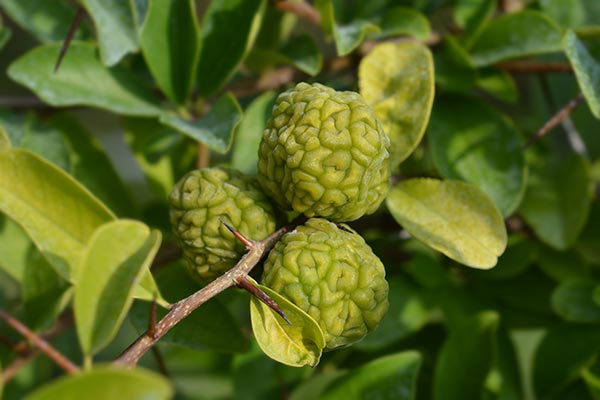

South Korean researchers examined the ability of Cudrania tricuspidata leaf extracts (CTEs) to protect against oxidative stress-mediated liver injury in vitro and in vivo. The results of their study were published in the Journal of Medicinal Food.
- The fruits, leaves and roots of C. tricuspidata contain large amounts of vitamins B and C and flavonoids.
- These nutrients allow it to exhibit various physiological activities, such as anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory effects. However, the hepatoprotective effects of C. tricuspidata extracts have not yet been investigated.
- To address this, the researchers used HepG2 cells and measured the cytoprotective effects of CTE through biochemical analysis.
- To assess CTE’s effects in vivo, they administered 250 and 500 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) CTE to mice for five days before giving them a single dose of acetaminophen (300 mg/kg).
- The researchers found that CTE increased antioxidant response element (ARE) luciferase activity compared with extracts from other parts of C. tricuspidata.
- CTE also upregulated the nuclear translocation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nfr2) and its target gene expression.
- Additionally, CTE inhibited the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cell death induced by arachidonic acid (AA) and iron (Fe) treatment in HepG2 cells.
- The researchers deduced that the cytoprotective effects of CTE may be due to kaempferol, the major flavonoid present in CTE.
- Kaempferol pre-treatment blocked AA+Fe-induced ROS production and reversed glutathione depletion, which led to decreased cell death.
- CTE also exerted protective effects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in both mice and HepG2 cells.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that CTE is a promising therapeutic candidate against oxidative stress-induced liver injury.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Cho SS, Yang JH, Seo KH, Shin SM, Park EY, Cho SS, Jo GU, Eo JH, Park JS, Oh DS, et al. CUDRANIA TRICUSPIDATA EXTRACT AND ITS MAJOR CONSTITUENTS INHIBIT OXIDATIVE STRESS-INDUCED LIVER INJURY. Journal of Medicinal Food. 07 June 2019;22(6):602–613. DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4322
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, Chinese mulberry, food cures, food is medicine, food science, functional food, herbal medicine, Herbs, kaempferol, liver damage, liver health, Mandarin melon berry, natural cures, natural medicine, oxidative stress, phytonutrients, prevention, remedies, research, TCM