Study: Eating foods high in healthy fats helps fight off skin cancer
10/13/2022 / By Zoey Sky
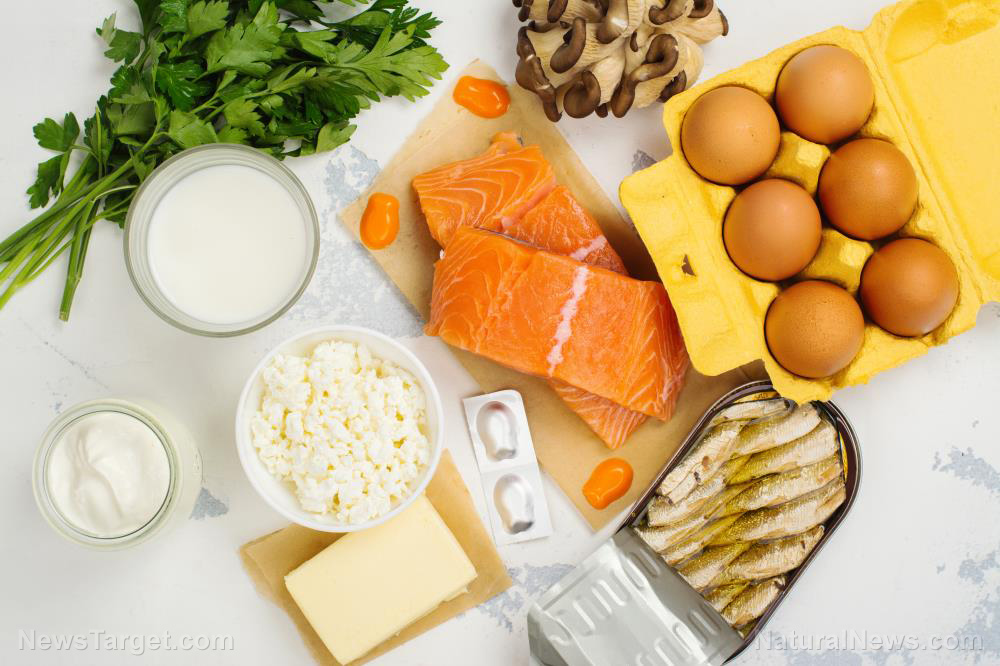

A study has found that foods rich in healthy fats can help protect against skin cancer and boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy among skin cancer patients.
Results showed that patients who followed the Mediterranean diet and received the drugs were more likely to survive and remain progression-free after 12 months.
The Mediterranean diet includes lots of superfoods like olive oil, nuts and fish, along with fruits, vegetables and whole grains. The diet is popular because it is associated with amazing health benefits such as a longer lifespan and protection against cardiovascular diseases.
Laura Bolte, a study author and dietician from the University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG) in the Netherlands, explained that the study “supports a role for dietary strategies to improve patient outcomes and survival.”
For the study, researchers from the U.K. and UMCG tracked the diets of 91 patients with advanced melanoma. The volunteers were all taking Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs). ICIs have worked well for those with melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer.
Researchers analyzed the patients’ progress and gave them frequent X-ray check ups. The findings revealed that the patients following a Mediterranean diet responded better to ICIs and were also most likely to not get any worse a year later.
Legumes and whole grains help reduce risk of experiencing side effects due to immunotherapy drugs
According to the results of the study, whole grains and legumes in particular also helped reduce the likelihood of patients experiencing side effects from the immunotherapy drugs kike colitis or inflammation of the colon.

Meanwhile, those who consumed a lot of red and processed meat experienced more side effects. (Related: Avoid sun damage with superfoods that offer photoprotective benefits for your skin.)
Bolte explained that the link between ICI response with diet and the gut microbiome “opens a promising and exciting future to enhance treatment responses.” She added that clinical trials studying the effect of a high-fiber diet, ketogenic diet and supplementation of omega-3 are also underway.
According to Bolte, since ICI therapy is being expanded to various tumor types, such as digestive cancers, future studies could help determine “treatment benefits for a large group of cancer patients in the future.”
As of writing, ongoing trials are being expanded to include other tumor types in digestive cancers.
ICIs, melanomas and cancer risk
ICI drugs work by blocking immune system checkpoints. This then forces the body’s own T cells, a type of white blood cell, to fight the cancer.
The American Cancer Society reported that the rates of melanoma have been growing significantly over the past years. According to estimates, at least 99,780 new melanomas will be diagnosed in the country this 2022.
Out of all these cases, 57,180 will be among men while 42,600 will be among women. At least 7,650 people are expected to die of melanoma, with an estimated 5,080 being men and 2,570 women.
Data suggests that you are more than 20 times more likely to get melanoma if you are White compared to if you are African American.
The lifetime risk of contracting melanoma is about 2.6 percent (one in 38) for those who are White, 0.1 percent (one in 1,000) for those who are Black and 0.6 percent (one in 167) for those who are Hispanic.
Melanoma is more common in men, but before age 50 it is more prevalent among women. Note that the older you are, the greater your risk of developing melanoma.
The average age of diagnosis is 65, but it is not unusual for those younger than 30 to develop melanoma. In fact, it is one of the more common cancers in young adults, especially among young women.
How to prevent melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. The disease spreads after the DNA in your skin cells is damaged, usually because of harmful UV rays, and then not repaired. This then triggers mutations that can form malignant tumors.
Causes of melanoma
- Family history – If other relatives have been diagnosed, then it increases your risk of getting melanoma.
- Hair color – Data suggests that redheads are more at risk of melanoma than others.
- Moles – The more moles you have, the greater the risk of being diagnosed with melanoma.
- Personal history – If you have had melanoma once, you are more likely to get it again.
- Skin type – Those with fairer skin have a higher risk of getting melanoma.
- Sun exposure – UV and UVB rays from the sun and tanning beds are bad for your skin.
Prevention
Practicing the healthy habits below can help protect against melanoma:
- If you’re spending time in the sun, use sunscreen and don’t overdo it.
- Avoid tanning outside and avoid tanning beds.
- Apply sunscreen at least 30 minutes before going outside when it’s sunny.
- Keep newborns out of the sun.
- Examine your skin every month.
- Consult your physician every year for a skin exam.
Tips for following a Mediterranean diet
Follow the tips below if you want to boost your overall health with the Mediterranean diet:
Foods to limit or avoid
Try to limit your consumption of these processed foods and ingredients when following the Mediterranean diet:
- Added sugar – Many foods contain added sugar, but the worst offenders are baked goods, candies, ice cream, soda, syrup and table sugar.
- Highly processed foods – Highly processed foods include convenience meals, fast food, granola bars and microwave popcorn.
- Processed meat – This includes beef jerky, deli meats, hot dogs and processed sausages.
- Refined grains – This includes chips, crackers, pasta, tortillas and white bread.
- Refined oils – Refined oils include canola oil, cottonseed oil, grapeseed oil and soybean oil.
- Trans fats – Fried foods, margarine and other processed foods contain trans fats.
Beverages
When on the Mediterranean diet, your go-to beverage should be water.
You can also drink moderate amounts of red wine or around one glass per day. Note that wine is optional and you should avoid it if you are pregnant, have difficulty drinking in moderation or are taking certain medications that may interact with alcohol.
Coffee and tea are healthy beverage choices, but it’s best to limit your use of added sugar or cream.
Limit your intake of sugar-sweetened beverages like soda or sweet tea because they are full of added sugar.
It’s fine to consume fruit juice in moderation, but it’s better to eat whole fruits to get the benefit of their dietary fiber content.
What to eat
There are variations between which foods are included in the Mediterranean diet in different countries.
While the diet examined by most studies contains a lot of healthy plant foods and is relatively low in animal products and meat, eating fish and seafood is recommended at least twice a week. The Mediterranean lifestyle also involves other healthy habits like exercising regularly, sharing meals with other people and minimizing stress levels.
If you don’t have fresh fruits and vegetables, you can cook with canned, dried or frozen fruits and vegetables.
Base your diet on these healthy Mediterranean foods:
- Eggs
- Dairy
- Fish and seafood
- Fruits
- Healthy fats
- Herbs and spices
- Legumes
- Nuts, nut butter and seeds
- Poultry
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
Follow the Mediterranean diet and eat foods rich in healthy fats to boost your overall well-being and prevent skin cancer.
Watch the video below to know how a Mediterranean diet can help boost your heart health.
This video is from the Vegan Shenanigan channel on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Battling skin cancer: Vitamin D may be used to boost anti-tumor activity, study finds.
Nutritious berries contain compounds that help fight cancer.
Botanical interventions for low-risk skin cancers.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
#nutrition, alternative medicine, cancer treatments, food cures, food is medicine, food science, functional food, Mediterranean diet, melanoma, natural cures, natural health, natural medicine, nutrients, skin cancer, skin health
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author